Analysis of the Relationship between Scleritis and T Cell Activation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with PD-1 Carrelizumab
- PMID: 36118947
- PMCID: PMC9467714
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4853481
Analysis of the Relationship between Scleritis and T Cell Activation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with PD-1 Carrelizumab
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Analysis of the Relationship between Scleritis and T Cell Activation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with PD-1 Carrelizumab.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9781974. doi: 10.1155/2023/9781974. eCollection 2023. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37547638 Free PMC article.
Abstract
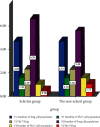
In order to explore the function of inhibiting the immune effect, the relationship between programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) carrelizumab in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma-induced scleritis and T cell activation is investigated. A total of 120 patients with primary liver cancer treated in the department of oncology of our hospital from July 2020 to January 2022 are selected and treated with carrelizumab. According to the occurrence of PD-1 carrelizumab treatment, the patients are divided into the scleritis group and nonscleritis group. The levels of T cells, PD-1, PD-L1 proteins, and serum inflammatory factors at different time points are compared. The experimental results show that the occurrence of scleritis after liver cancer treatment with PD-1 carrelizumab is closely associated with Treg cells, the percentage of Th17 cells, the expression of PD-1, PD-L1 proteins, and inflammatory factors. It is clearly evident that PD-1 carrelizumab can increase the risk of scleritis by affecting T cell activation.
Copyright © 2022 Yazhen Yuan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Health Commission of Prc. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition) Chin J Dis . 2022;35(1)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials