The impact of Rituximab administered before transplantation in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A real-world study
- PMID: 36119024
- PMCID: PMC9471377
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.967026
The impact of Rituximab administered before transplantation in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A real-world study
Abstract
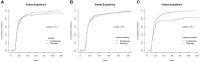
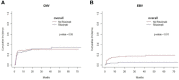
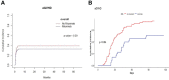
Rituximab is used to eliminate B cells as a chimeric monoclonal antibody directed against CD20, a B-cell antigen expressed on B cells. To explore the impact of rituximab administered before transplantation, we implemented a retrospective, monocentric study and utilized real-world data collected at our center between January 2018 and December 2020, and then followed until December 2021. Based on whether a dose of 375mg/m2 rituximab was used at least once within two weeks before transplantation, patients undergoing allo-HSCT were classified into two groups: rituximab (N=176) and non-rituximab (N=344) group. Amongst all the patients, the application of rituximab decreased EBV reactivation (P<0.01) and rituximab was an independent factor in the prevention of EBV reactivation by both univariate and multivariate analyses (HR 0.56, 95%CI 0.33-0.97, P=0.04). In AML patients, there were significant differences in the cumulative incidence of aGVHD between the two groups (P=0.04). Our data showed that rituximab was association with a decreased incidence of aGVHD in AML patients according to both univariate and multivariate analyses. There was no difference between the two groups in other sets of populations. Thus, our study indicated that rituximab administered before transplantation may help prevent EBV reactivation in all allo-HSCT patients, as well as prevent aGVHD in AML patients after allo-HSCT.
Keywords: B cell; EBV - Epstein-Barr virus; aGVHD: acute graft vs host disease; allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; prior to transplantation; rituximab.
Copyright © 2022 Wei, Xie, Jiang, Li, Wu, Zhang, Li, Zhou, Ma, Tang, He, Wu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

