Ciltacabtagene autoleucel: The second anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapeutic armamentarium of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma
- PMID: 36119032
- PMCID: PMC9479060
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.991092
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel: The second anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapeutic armamentarium of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma
Abstract
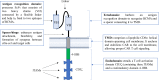
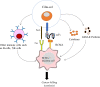
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel (also known as cilta-cel) is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) on the surface of cancer cells in B cell malignancies, such as multiple myeloma (MM). It is a second-generation CAR that is outfitted with an ectodomain comprising two BCMA-binding single chain variable fragment (ScFv) domains, a transmembrane domain, and an endodomain possessing CD3ζ and 4-1BB. Cilta-cel is an autologous, gene-edited CAR T-cell that is prepared by collecting and modifying the recipient's T-cells to create a patient personalized treatment in the laboratory to be infused back. This CAR T-cell product exceptionally entails CARs with two BCMA-targeting single-domain antibodies that detect two epitopes of BCMA expressed on the malignant cells of MM. Cilta-cel is the current addition to the treatment armamentarium of relapsed or refractory (r/r) MM after its approval by the FDA on February 28, 2022, based on the results of the Phase 1b/2 CARTITUDE-1 study. It was the second approved anti-BCMA CAR T-cell product after idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel) to treat myeloma patients. It induces early, deep, and long-lasting responses with a tolerable safety profile in r/r MM. Cilta-cel-treated myeloma patients may potentially experience adverse effects ranging from mild to life-threatening, but they are mostly manageable toxicities. Besides, it has a consistent safety profile upon a longer follow-up of patients. Cilta-cel generally outperforms ide cel in terms of efficacy in MM, but shows comparable adverse events. This review highlights the current updates on cilta-cel efficacy, adverse events, comparison with ide-cel, and its future direction in the treatment of MM.
Keywords: CAR T-cell therapy; adverse effects; cilta-cel; efficacy; multiple myeloma.
Copyright © 2022 Chekol Abebe, Yibeltal Shiferaw, Tadele Admasu and Asmamaw Dejenie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gross G, Gorochov G, Waks T, Eshhar Z. Generation of effector T cells expressing chimeric T cell receptor with antibody type-specificity. Transplant Proc (1989) 21(1 Pt 1):127–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

