Increased serum level of alpha-2 macroglobulin and its production by B-lymphocytes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 36119042
- PMCID: PMC9478581
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.953644
Increased serum level of alpha-2 macroglobulin and its production by B-lymphocytes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
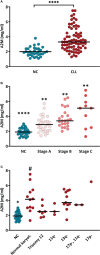
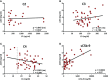
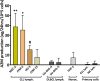
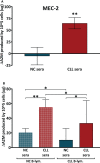
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), the most common adult's leukemia in the western world, is caused in 95% of the cases by uncontrolled proliferation of monoclonal B-lymphocytes. The complement system in CLL is chronically activated at a low level via the classical pathway (CP). This chronic activation is induced by IgG-hexamers, which are formed after binding to alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M). The study investigated for the first time the serum levels of A2M in CLL patients, their association with the disease severity, and A2M production by the malignant B-lymphocytes. Blood samples were collected from 65 CLL patients and 30 normal controls (NC) subjects, and used for quantifications of the A2M levels, the complement activation marker (sC5b-9), the complement components C2, C3 and C4, and clinical biochemistry and hematology parameters. The production of A2M was studied in B-lymphocytes isolated from blood samples as well as in CLL and non-CLL cell lines.The serum A2M levels were significantly higher in CLL patients vs NCs, showing values of 3.62 ± 0.22 and 1.97 ± 0.10 mg/ml, respectively. Within the CLL group, A2M levels correlated significantly with the disease stage, with sC5b-9, and with clinical indicators of the disease severity. Increased A2M production was showed in three out of four CLL B-lymphocytic lines that were studied, as compared to non-CLL lines, to a non-lymphocytic line, and to blood-derived primary B-lymphocytes. A2M production was further increased both in primary cells and in the CLL cell-line after incubation with CLL sera, compared to NC sera. This study shows for the first time that serum A2M levels in CLL are significantly increased, likely due to A2M production by the malignant B-lymphocytes, and are correlated with the disease severity and with chronic complement activation. The moderate change in A2M production after incubation with NC sera in-vitro supports the hypothesis that inhibition of excess A2M production can be achieved, and that this may potentially down-regulate the IgG-hexamerization and the resulting chronic CP activation. This may also help restore complement system activity, and eventually improve complement activity and immunotherapy outcomes in CLL.
Keywords: B-lymphocytes; alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M); chronic lymphocytic leukemia; classical pathway of complement; complement system.
Copyright © 2022 Michelis, Milhem, Galouk, Stemer, Aviv, Tadmor, Shehadeh, Shvidel, Barhoum and Braester.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Naseraldeen N, Michelis R, Barhoum M, Chezar J, Tadmor T, Aviv A, et al. . The role of alpha 2 macroglobulin in IgG-aggregation and chronic activation of the complement system in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Front Immunol (2021) 11:603569. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.603569 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

