The potential roles of interleukin-25 in infectious diseases
- PMID: 36119076
- PMCID: PMC9478665
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.986118
The potential roles of interleukin-25 in infectious diseases
Abstract
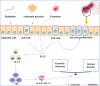
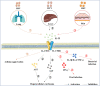
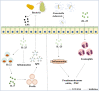
Interleukin-25 (IL-25), also known as IL-17E, is a recently identified cytokine of the IL-17 family. Numerous studies illustrated that the expression of IL-25 is regulated by multiple pathogens, including parasitic, viral, and bacterial infections. IL-25 has a dual function in infectious diseases. On the one hand, IL-25 activates type 2 immunity via the relevant cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which are associated with the development of pathogenic infection-related allergic diseases. On the other hand, IL-25 involves in the recruitment of group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) to enhanced T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation, which are important to the clearance of pathogens. However, the precise roles of IL-25 in infectious diseases remain largely unknown. Thus, the current review will shed light on the pivotal roles of IL-25 in infectious diseases.
Keywords: IL-17 family; IL-25; Th2; infectious diseases; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Zhang, Tao, Nawaz, Chen and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-17 family cytokines in protective immunity against infections: role of hematopoietic cell-derived and non-hematopoietic cell-derived interleukin-17s.Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Jan;62(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12560. Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29205464 Review.
-
Role of type 2 innate lymphoid cell and its related cytokines in tumor immunity.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Apr;235(4):3249-3257. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29287. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31625163 Review.
-
Clinical relevance and therapeutic potential of IL-38 in immune and non-immune-related disorders.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2022 Sep 1;33(3):54-69. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2022.0480. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2022. PMID: 37052152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic memory type Th2 cells in allergic inflammation.Trends Immunol. 2014 Feb;35(2):69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Trends Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24332592 Review.
-
Essential, dose-dependent role for the transcription factor Gata3 in the development of IL-5+ and IL-13+ type 2 innate lymphoid cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jun 18;110(25):10240-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217158110. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23733962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Critical and diverse role of alarmin cytokines in parasitic infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 4;14:1418500. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1418500. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39559705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin 25 and its biological features and function in intestinal diseases.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022;47(4):362-372. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2022.124416. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36817397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intricate Crosstalk Between Food Allergens, Phages, Bacteria, and Eukaryotic Host Cells of the Gut-skin Axis.Yale J Biol Med. 2024 Sep 30;97(3):309-324. eCollection 2024 Sep. Yale J Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39351325 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of innate lymphoid cell by microbial metabolites.J Mol Med (Berl). 2025 May;103(5):491-509. doi: 10.1007/s00109-025-02530-3. Epub 2025 Mar 25. J Mol Med (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40128460 Review.
-
Trained immunity of intestinal tuft cells during infancy enhances host defense against enteroviral infections in mice.EMBO Mol Med. 2024 Oct;16(10):2516-2538. doi: 10.1038/s44321-024-00128-9. Epub 2024 Sep 11. EMBO Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39261649 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

