Pulse oximetry vs non-invasive blood pressure/oscillometry to record blood pressure in neonates: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 36119154
- PMCID: PMC9480655
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1381_21
Pulse oximetry vs non-invasive blood pressure/oscillometry to record blood pressure in neonates: A prospective observational study
Abstract
Aim: To assess the usefulness and efficacy of pulse oximetry (disappearance/reappearance of plethsmographic waves) as a method of non-invasive blood pressure monitoring in neonates.
Objective: To investigate the reliability of the plethysmographic wave form of the pulse oximeter to measure the systolic blood pressure.
Study setting: A prospective observational study was done to assess usefulness and efficacy of pulse oximetry (disappearance/reappearance of plethysmographic waves) as a method of non-invasive blood pressure monitoring in neonates.
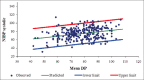
Material and methods: The study was conducted among 500 neonates to investigate the reliability of the plethysmographic waveform of the pulse oximeter to measure the systolic blood pressure as it is a easy way to perform and non invasive.
Statistical analysis used: The results will compare and analyse statistically by Pearson correlation co-efficient. Regression modeling will carried out to explain the relationship of non-invasive blood pressure with mean DP and RP and attempted to predict the non-invasive blood pressure from mean DP/mean RP.
Results: The study results revealed that NIBP systolic and diastolic both correlated with DP and RP of pulse oximetry plethysmograph.
Conclusion: Study concluded that pulse oximetry is a reliable tool in measuring blood pressure in neonates (appearance and disappearance of plethysmogram).
Keywords: Intra-arterial pressure; measurement location; non-invasive measurement; oscillometric device; pulse oximetry.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Report of the Second Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children -1987. Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, Maryland. Paediatrics. 1987;79:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Matsuoka OT, Pinheiro AC, Pascuas DZ, Leone CR. Evolution of systemic arterial blood pressure during neonatal period in term newborns adequate for gestacional age. J Pediatr (Rio J) 1996;72:155–8. - PubMed
-
- Pilossoff V, Schöber JG, Peters D, Bühlmeyer K. Non-invasive oscillometric measurement of systolic, mean and diastolic blood pressure in infants with congenital heart defects after operation. A comparison with direct blood pressure measurements. Eur J Pediatr. 1985;144:324–30. - PubMed
-
- Lui K, Doyle PE, Buchanan N. Oscillometric and intra-arterial blood pressure measurements in the neonate:Acomparison of methods. JPaediatrChild Health. 1982;18:32–4. - PubMed
-
- Pilossoff V, Schöber JG, Peters D, Bühlmeyer K. Non-invasive oscillometric measurement of systolic, mean and diastolic blood pressure in infants with congenital heart defects after operation. A comparison with direct blood pressure measurements. Eur J Pediatr. 1985;144:324–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources