Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Arnebiae Radix and Dictamni Cortex and efficacy study of herbal extracts on allergic contact dermatitis using 3D human reconstructed epidermis
- PMID: 36119360
- PMCID: PMC9476703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chmed.2021.10.006
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Arnebiae Radix and Dictamni Cortex and efficacy study of herbal extracts on allergic contact dermatitis using 3D human reconstructed epidermis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the quality of Arnebiae Radix (AR) and Dictamni Cortex (DC) and study the efficacy of herbal extracts of these two herbs on the treatment of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
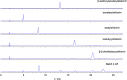
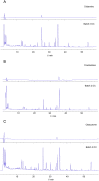
Methods: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of effective components was performed using High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC), High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), and HPLC-Quadrupole Time of Flight-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-QTOF-MS). In vitro allergic ACD 3D model was established by incubating 3D reconstructed human epidermis (RHE) with skin sensitizer, potassium dichromate. A total of 65 gene expression that were associated with ACD, which included 24 antioxidant responsive element (ARE) and 41 SENS-IS genes were quantified by qRT-PCR. More than or equal to 10 ARE genes and 18 SENN-IS genes were induced by 1.3-fold, demonstrating the successful establishment of in vitro ACD model. Oil extracts of AR and DC were applied on the in vitro ACD model to study the efficacy.
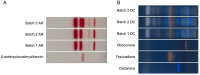
Results: Batch 3 of AR and batch 2 of DC showed presence of all active ingredients with the highest concentrations. Active ingredients of the herbs were extracted using a special oil and formulated into herbal oil extracts. The herbal oil extracts were able to down regulate the induced genes in the in-vitro ACD skin model, bringing the tissue back to homeostatic status.
Conclusion: The oil extracts showed the potent efficacy of using AR and DC in ACD treatment. The combination study will be done to optimize the formulation ratio which will be developed into a topical cream.
Keywords: 3D reconstructed epidermis; Arnebiae Radix; Chinese medicine; Dictamni Cortex; allergic contact dermatitis; quality control.
© 2021 Tianjin Press of Chinese Herbal Medicines. Published by ELSEVIER B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prinsepia utilis Royle leaf extract: Ameliorative effects on allergic inflammation and skin lesions in allergic contact dermatitis and polyphenolic profiling through UPLC-MS/MS coupled to chemometric analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;305:116093. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116093. Epub 2023 Jan 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36603785
-
An integrated data filtering and identification strategy for rapid profiling of chemical constituents, with Arnebiae Radix as an example.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Oct 11;1629:461496. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461496. Epub 2020 Aug 18. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 32846341
-
Radix Saposhnikovia extract suppresses mouse allergic contact dermatitis by regulating dendritic-cell-activated Th1 cells.Phytomedicine. 2015 Dec 1;22(13):1150-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Phytomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26598913
-
[Advances in studies on chemical compositions and pharmacological activities of Arnebiae Radix].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Nov;40(21):4127-35. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 27071244 Review. Chinese.
-
Allergic and irritant contact dermatitis.Eur J Dermatol. 2009 Jul-Aug;19(4):325-32. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2009.0686. Eur J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19447733 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Screening of Chemical Constituents in the Traditional Chinese Medicine Arnebiae Radix by UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry.Molecules. 2022 Apr 19;27(9):2631. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092631. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35565981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlström M.G., Thyssen J.P., Wennervaldt M., Menné T., Johansen J.D. Nickel allergy and allergic contact dermatitis: A clinical review of immunology, epidemiology, exposure, and treatment. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81(4):227–241. - PubMed
-
- Alinaghi F., Bennike N.H., Egeberg A., Thyssen J.P., Johansen J.D. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80(2):77–85. - PubMed
-
- Barbaud A. Mechanism and diagnosis of protein contact dermatitis. Current Opinion on Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2020;20(2):117–121. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Xian Y.F., Loo S., Chan W.Y., Liu L., Lin Z.X. Anti-atopic dermatitis effects of dictamni cortex: Studies on in vitro and in vivo experimental models. Phytomedicine. 2021;82 - PubMed
-
- Cottrez F., Boitel E., Auriault C., Aeby P., Groux H. Genes specifically modulated in sensitized skins allow the detection of sensitizers in a reconstructed human skin model. Development of the SENS-IS assay. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015;29(4):787–802. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

