Recovery of value-added anthocyanins from mulberry by a cation exchange chromatography
- PMID: 36119370
- PMCID: PMC9475210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.08.022
Recovery of value-added anthocyanins from mulberry by a cation exchange chromatography
Abstract
Anthocyanins are often targets in polyphenol analysis. However, it's hard to effectively separate anthocyanin from copigments such as phenolic acid and flavanols due to their similar structure. Thus, a cation exchange chromatography with 001 × 7 has been developed, which is available for anthocyanins isolation both on a small and large scale. The optimal process condition of anthocyanins isolation was determined. Compared to the macroporous adsorbent resins and Strong Cation Exchange resin (SCX), 001X7 shows greater economic advantages in large-scale purification of anthocyanins. More than 95% purity of the anthocyanin fraction can be achieved through this approach. This method shows a path to provide large quantities of copigments-free anthocyanins from mulberry polyphenols for the further study of its biological effects and may be extended to other analytical methods of polyphenol isolation from other plant materials.
Keywords: 001X7; Anthocyanins; Column chromatography; Copigments; Isolation; Scale-up.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




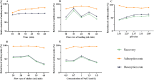
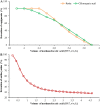

References
-
- Ahmadiani N., Sigurdson G.T., Robbins R.J., Collins T.M., Giusti M.M. Solid phase fractionation techniques for segregation of red cabbage anthocyanins with different colorimetric and stability properties. Food Res. Int. 2019;120:688–696. - PubMed
-
- Blum U. Springer International Publishing. 2019. Simple phenolic acids in solution culture I: pH and pKa; pp. 71–113.
-
- Chen Y., Du F., Wang W., Li Q., Zheng D.H., Zhang W.J., Zhao T., Mao G.H., Feng W.W., Wu X.Y., Yang L.Q. Large-scale isolation of high-purity anthocyanin monomers from mulberry fruits by combined chromatographic techniques. J. Separ. Sci. 2017;40(17):3506–3512. - PubMed
-
- da Silva L.F., Guerra C.C., Klein D., Bergold A.M. Solid cation exchange phase to remove interfering anthocyanins in the analysis of other bioactive phenols in red wine. Food Chem. 2017;227:158–165. - PubMed
-
- Du Q., Zheng J., Xu Y. Composition of anthocyanins in mulberry and their antioxidant activity. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008;21(5):390–395.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

