A high preoperative serum IL-25 level is a negative prognosis predictor after liver resection for HBV-HCC
- PMID: 36119529
- PMCID: PMC9478489
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.858151
A high preoperative serum IL-25 level is a negative prognosis predictor after liver resection for HBV-HCC
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between preoperative IL-25 levels and HBV-HCC patient outcomes following liver surgery.
Methods: This study enrolled consecutive HCC patients that had undergone liver surgery from 2008 to 2015. Baseline patient clinical properties were assessed to establish predictors of postoperative overall survival and recurrence-free survival (OS and RFS, respectively) following liver resection. In addition, serum IL-25 levels were assessed via ELISA.
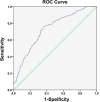
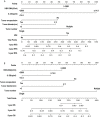
Results: Cox regression analyses revealed IL-25 levels to be independently related to the OS and RFS of 896 HBV-associated HCC patients. An optimal IL-25 cutoff level of 14.9 μg/ml was identified, with 206 patients in this cohort having IL-25 levels above this threshold. Both the OS and RFS of patients with an IL-25 level <14.9 μg/ml were significantly better after liver resection as compared to those of patients with higher preoperative levels of this cytokine (p < 0.05). Cox multivariate regression analyses revealed an IL-25 level ≥ 14.9 μg/L to be an independent predictor of poorer RFS and OS. A combination of IL-25 levels and tumor diameter may be an even more reliable predictor of OS.
Conclusions: IL-25 levels are independent predictors of postoperative survival within HCC patients undergoing liver resection.
Keywords: IL-25; biomarker; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
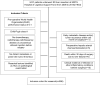
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Relationship Between Serum Interleukin-6 and the Recurrence of Hepatitis B Virus Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Jun;94(24):e941. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000941. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26091457 Free PMC article.
-
Association of family history with long-term prognosis in patients undergoing liver resection of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019 Apr;8(2):88-100. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.11.20. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31098356 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio predicts survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 14;21(38):10898-906. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10898. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26478681 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral therapy improves post-operative survival outcomes in patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma of less than 3 cm - A retrospective cohort study.Am J Surg. 2020 Apr;219(4):717-725. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2019.05.016. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Am J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31266631
-
Impact of viral hepatitis on outcomes after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: results from a north american center.Ann Surg Oncol. 2014 Aug;21(8):2708-16. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3609-6. Epub 2014 May 8. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24806113
Cited by
-
Interleukin-25 as a Potential Biomarker in Lung Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with HBV History in Chinese Patients: A Single Center, Case-control Study.Int J Med Sci. 2024 May 19;21(7):1337-1343. doi: 10.7150/ijms.90642. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38818476 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative predictors of outcome of hepatectomy for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 13;13:1230164. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1230164. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37519791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine biomarkers for independent prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 29;16(1):421. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02188-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40155531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

