Current status of perimesencephalic non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- PMID: 36119687
- PMCID: PMC9475169
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.960702
Current status of perimesencephalic non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
Abstract
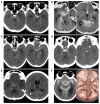
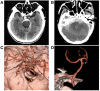
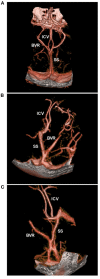
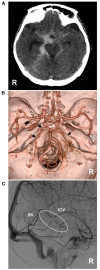
Perimesencephalic nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (PNSAH) is a distinctive disease, representing SAH centered in perimesencephalic cisterns, with negative angiography findings. In recent years, the number of patients with PNSAH has increased significantly; however, the knowledge of PNSAH is insufficient. Therefore, we performed a review of the literature from a PubMed search and recounted our understanding of PNSAH. In this review, we summarized that current high-resolution computed tomography angiography is an acceptable replacement for digital subtraction angiography to rule out aneurysms in PNSAH with strict criteria. The current hypothesis about the etiology of PNSAH is that there is deep vein rupture from aberrant venous anatomy and increased intracranial venous pressure. PNSAH is associated with mild symptoms and lower rates of hydrocephalus and symptomatic vasospasm. For PNSAH, conservative treatment has been the mainstream treatment. PNSAH has a benign clinical course and an excellent prognosis; in long-term follow-up, re-bleeding and death were uncommon.
Keywords: complication; etiology; perimesencephalic non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage; prognosis; review.
Copyright © 2022 Hou and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nguyen I, Caton MT, Tonetti D, Abla A, Kim A, Smith W, et al. . Angiographically occult subarachnoid hemorrhage: yield of repeat angiography, influence of initial CT bleed pattern, and sources of diagnostic error in 242 consecutive patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2022). 10.3174/ajnr.A7483 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

