Didymin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress
- PMID: 36120130
- PMCID: PMC9476736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chmed.2021.07.002
Didymin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress
Abstract
Objective: This study was designed to investigate the protective effects of didymin (Did) on doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiotoxicity.
Methods: After pretreatment with Did (2, 4, 8 mg/kg intraperitoneal i.p.) for 7 d, the male C57 mice were injected with single dose of DOX (20 mg/kg i.p.). The cardioprotective effect of Did was observed on the 7th day after DOX treatment.
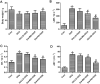
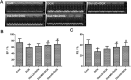
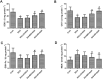
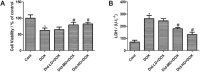
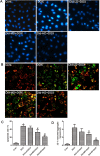
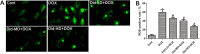
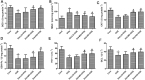
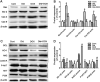
Results: DOX delayed body growth and caused cardiac tissue injury, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Similar experiments in H9C2 cardiomyocytes showed that DOX reduced cell viability, increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and fragmentation of DNA, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, and induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. However, all of these adverse effects were suppressed by Did pretreatment. Did increased protein expression of glutamate-L-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCL), heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Besides, Did also induced activation of PI3K/AKT.
Conclusion: These findings indicated Did prevented DOX-induced cardiac injury and apoptosis via activating PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Nrf2; PI3K/Akt; cardiotoxicity; didymin; doxorubicin.
© 2021 Tianjin Press of Chinese Herbal Medicines. Published by ELSEVIER B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Benjanuwattra J., Siri-Angkul N., Chattipakorn S.C., Chattipakorn N. Doxorubicin and its proarrhythmic effects: A comprehensive review of the evidence from experimental and clinical studies. Pharmacological Research. 2020;151 - PubMed
-
- Catanzaro M.P., Weiner A., Kaminaris A., Li C., Cai F., Zhao F.…Liang Q. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte death is mediated by unchecked mitochondrial fission and mitophagy. FASEB Journal: Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2019;33:11096–11108. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, R.C., Xu, X.D., Liu, X. Z., Sun, G.B., Zhu, Y.D., Dong, X., Wang, J., Zhang, H.J., Zhang, Q., Sun, X.B. (2015). Total flavonoids from Clinopodium chinense (Benth.) O. Ktze protect against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: Ecam, 2015: 472565. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

