APOE and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Markers in Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- PMID: 36123141
- PMCID: PMC9576291
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200851
APOE and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Markers in Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
Background and objective: We investigated the associations between the APOE genotype, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), and neuroimaging markers of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
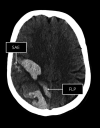
Methods: We included patients from a prospective, multicenter UK observational cohort study of patients with ICH and representative UK population controls. First, we assessed the association of the APOE genotype with ICH (compared with controls without ICH). Second, among patients with ICH, we assessed the association of APOE status with the hematoma location (lobar or deep) and brain CT markers of CAA (finger-like projections [FLP] and subarachnoid extension [SAE]).
Results: We included 907 patients with ICH and 2,636 controls. The mean age was 73.2 (12.4 SD) years for ICH cases vs 69.6 (0.2 SD) for population controls; 50.3% of cases and 42.1% of controls were female. Compared with controls, any APOE ε2 allele was associated with all ICH (lobar and nonlobar) and lobar ICH on its own in the dominant model (OR 1.38, 95% CI 1.13-1.7, p = 0.002 and OR 1.50, 95% CI 1.1-2.04, p = 0.01, respectively) but not deep ICH in an age-adjusted analyses (OR 1.26, 95% CI 0.97-1.63, p = 0.08). In the cases-only analysis, the APOE ε4 allele was associated with lobar compared with deep ICH in an age-adjusted analyses (OR 1.56, 95% CI 1.1-2.2, p = 0.01). When assessing CAA markers, APOE alleles were independently associated with FLP (ε4: OR 1.74, 95% CI 1.04-2.93, p = 0.04 and ε2/ε4: 2.56, 95% CI 0.99-6.61, p = 0.05). We did not find an association between APOE alleles and SAE.
Discussion: We confirmed associations between APOE alleles and ICH including lobar ICH. Our analysis shows selective associations between APOE ε2 and ε4 alleles with FLP, a CT marker of CAA. Our findings suggest that different APOE alleles might have diverging influences on individual neuroimaging biomarkers of CAA-associated ICH.
© 2022 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Burn J, Warlow C. A prospective study of acute cerebrovascular disease in the community: the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project: 1981-86. 2. Incidence, case fatality rates and overall outcome at one year of cerebral infarction, primary intracerebral and subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990;53(1):16-22. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der Tweel I, Algra A, Klijn CJ. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(2):167-176. - PubMed
-
- Moulin S, Labreuche J, Bombois S, et al. Dementia risk after spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(8):820-829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous