Patient-reported outcomes from a randomized trial of neoadjuvant atezolizumab-chemotherapy in early triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 36123366
- PMCID: PMC9485121
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-022-00457-3
Patient-reported outcomes from a randomized trial of neoadjuvant atezolizumab-chemotherapy in early triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
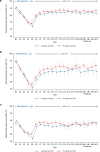
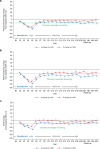
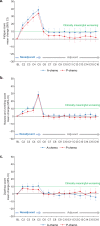
Patient-reported outcomes data assessing patients' experience of immunotherapy treatment burden in potentially curable early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) are lacking. These patient-reported data inform clinical benefit and decision-making for adding atezolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in early-stage TNBC. IMpassion031 (NCT03197935) randomly assigned patients with stage II/III TNBC (T2-T4d primary tumors) to 5 cycles (4 weeks/cycle) of every 2-week neoadjuvant atezolizumab 840 mg or placebo with weekly nab-paclitaxel (3 cycles) followed by every 2-week dose-dense doxorubicin+cyclophosphamide (2 cycles). After surgery, the atezolizumab-chemotherapy arm received atezolizumab 1200 mg every 3 weeks (11 cycles). The placebo-chemotherapy arm was observed under standard of care. To assess treatment burden from the patients' perspective, which comprised measures of the treatment-related impact on patients' functioning and health-related quality of life (HRQoL), as well as patients' experience of treatment-related symptoms plus their associated bother, patients completed the EORTC QLQ-C30 and FACT-G single-item GP5. Predefined secondary endpoints included mean and mean change from baseline values in the QLQ-C30 function (role and physical) and global health status/quality of life scales. Exploratory endpoints included mean and mean change from baseline in treatment-related symptoms, and treatment side effect bother. Mean physical, role function, and HRQoL were similar between arms at baseline and throughout treatment. In the neoadjuvant period, both arms exhibited clinically meaningful declines of similar magnitude from baseline in physical, role function, and HRQoL, and reported similar treatment side effect to bother at each visit. Improved pathologic complete response from adding atezolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage TNBC occurred without imposing additional treatment burden on patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors received support from Genentech, Inc., during the conduct of the study. Editorial support provided by an independent medical writer, under the guidance of the authors, was funded by the sponsor. The authors declare no competing non-financial interests except as noted below. C.H.B. reports institutional grants and research support from Pfizer, Novartis, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Roche/Genentech, Lilly, Sanofi, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Mylan, Merrimack, Merck, AbbVie, Astellas Pharma, BioMarin, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Abraxis Biosciences, AB Science, Asana Biosciences, Medivation, Exelixis, ImClone Systems, LEO Pharma, and Millennium; and fees for serving on advisory boards and consulting from Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Eisai, Bayer, MSD, and AstraZeneca. S.S. has received speaking and consulting fees from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, and Novartis; and speaking fees and/or grants from Lilly, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, MSD, Eisai, Takeda, and Taiho. N.H. has received personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, and Roche. H.Z. has received consulting fees from Roche/Genentech. K.H.J. has received personal fees from Roche, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Takeda, and Celgene. She.P. and Shi.P. are employees and stockholders of Roche/Genentech. A.N.D is an employee of Roche and has a patent pending relevant to this work. M.L.-H. is an employee and stockholder of Roche. S.Y.C. is an employee of and stockholder in Roche/Genentech and has a patent pending relevant to this work. E.A.M. reports research support from GSK; honoraria from Physicians’ Education Resource; compensation for serving on advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Exact Sciences, Merck, Peregrine Pharmaceuticals, Roche/Genentech, SELLAS Life Sciences, and TapImmune; institutional support from AstraZeneca, EMD Serono, Galena Biopharma, and Roche/Genentech; and serving as an uncompensated steering committee member for Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, and Roche/Genentech.
Figures

References
-
- Howlader N, et al. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2014. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

