Annual Research Review: Developmental pathways linking early behavioral inhibition to later anxiety
- PMID: 36123776
- PMCID: PMC10690832
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpp.13702
Annual Research Review: Developmental pathways linking early behavioral inhibition to later anxiety
Abstract
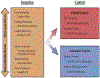
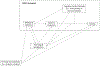
Behavioral Inhibition is a temperament identified in the first years of life that enhances the risk for development of anxiety during late childhood and adolescence. Amongst children characterized with this temperament, only around 40 percent go on to develop anxiety disorders, meaning that more than half of these children do not. Over the past 20 years, research has documented within-child and socio-contextual factors that support differing developmental pathways. This review provides a historical perspective on the research documenting the origins of this temperament, its biological correlates, and the factors that enhance or mitigate risk for development of anxiety. We review as well, research findings from two longitudinal cohorts that have identified moderators of behavioral inhibition in understanding pathways to anxiety. Research on these moderators has led us to develop the Detection and Dual Control (DDC) framework to understand differing developmental trajectories among behaviorally inhibited children. In this review, we use this framework to explain why and how specific cognitive and socio-contextual factors influence differential pathways to anxiety versus resilience.
Keywords: Temperament; anxiety; child development; developmental psychopathology; electroencephalography.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

Comment in
-
The developmental psychopathology of detection and dual control - a commentary on Fox et al. (2023).J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;64(4):562-565. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13771. Epub 2023 Feb 27. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36847558
Similar articles
-
A Neurobehavioral Mechanism Linking Behaviorally Inhibited Temperament and Later Adolescent Social Anxiety.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017 Dec;56(12):1097-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Oct 13. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 29173744 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Emergence of Social Anxiety in Children With Behavioral Inhibition.Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 1;89(7):681-689. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.10.004. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33353668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infant behavioral inhibition predicts personality and social outcomes three decades later.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 5;117(18):9800-9807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917376117. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32312813 Free PMC article.
-
Early Childhood Predictors of Anxiety in Early Adolescence.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2019 Jul;47(7):1121-1133. doi: 10.1007/s10802-018-0495-6. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30569254
-
Linking temperamental fearfulness and anxiety symptoms: a behavior-genetic perspective.Biol Psychiatry. 2000 Dec 15;48(12):1199-209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)01003-9. Biol Psychiatry. 2000. PMID: 11137060 Review.
Cited by
-
Symptoms of Selective Mutism in Middle Childhood: Psychopathological and Temperament Correlates in Non-clinical and Clinically Referred 6- to 12-year-old Children.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024 Dec;55(6):1514-1525. doi: 10.1007/s10578-023-01512-1. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024. PMID: 36853426 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrative Model of Youth Anxiety: Cognitive-Affective Processes and Parenting in Developmental Context.Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2023 Dec;26(4):1025-1051. doi: 10.1007/s10567-023-00458-z. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37819403
-
Preliminary perceived intervention changes and engagement in an evidence-based program targeted at behavioral inhibition during early childhood, delivered in-person and online.Front Psychol. 2023 May 26;14:1187255. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1187255. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37303908 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal neural responses to novelty related to behavioral inhibition at 1 year.Dev Psychol. 2024 Nov;60(11):2062-2070. doi: 10.1037/dev0001654. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Dev Psychol. 2024. PMID: 37971828
-
Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia, Effortful Control, and Child Social Anxiety Symptoms.Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2024 Sep;52(9):1441-1453. doi: 10.1007/s10802-024-01202-z. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2024. PMID: 38668930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aktar E, Majdandžić M, de Vente W, & Bögels SM (2013). The interplay between expressed parental anxiety and infant behavioural inhibition predicts infant avoidance in a social referencing paradigm: Expressed parental anxiety and infant behavioural inhibition. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54, 144–156. - PubMed
-
- Aktar E, Majdandžić M, de Vente W, & Bögels SM (2014). Parental social anxiety disorder prospectively predicts toddlers’ fear/avoidance in a social referencing paradigm. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 55, 77–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

