mRNA isoform balance in neuronal development and disease
- PMID: 36123820
- PMCID: PMC10024649
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1762
mRNA isoform balance in neuronal development and disease
Abstract
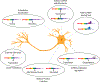
Balanced mRNA isoform diversity and abundance are spatially and temporally regulated throughout cellular differentiation. The proportion of expressed isoforms contributes to cell type specification and determines key properties of the differentiated cells. Neurons are unique cell types with intricate developmental programs, characteristic cellular morphologies, and electrophysiological potential. Neuron-specific gene expression programs establish these distinctive cellular characteristics and drive diversity among neuronal subtypes. Genes with neuron-specific alternative processing are enriched in key neuronal functions, including synaptic proteins, adhesion molecules, and scaffold proteins. Despite the similarity of neuronal gene expression programs, each neuronal subclass can be distinguished by unique alternative mRNA processing events. Alternative processing of developmentally important transcripts alters coding and regulatory information, including interaction domains, transcript stability, subcellular localization, and targeting by RNA binding proteins. Fine-tuning of mRNA processing is essential for neuronal activity and maintenance. Thus, the focus of neuronal RNA biology research is to dissect the transcriptomic mechanisms that underlie neuronal homeostasis, and consequently, predispose neuronal subtypes to disease. This article is categorized under: RNA in Disease and Development > RNA in Disease RNA in Disease and Development > RNA in Development.
Keywords: RNA binding protein; alternative polyadenylation; alternative splicing; neurodevelopment; neuronal health.
© 2022 The Authors. WIREs RNA published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures


References
-
- Akamatsu W, Okano Hirotaka J, Osumi N, Inoue T, Nakamura S, Sakakibara S-I, . . . Okano H. (1999). Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 96(17), 9885–9890. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9885 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akawi NA, Ben-Salem S, Hertecant J, John A, Pramathan T, Kizhakkedath P, . . . Al-Gazali L. (2016). A homozygous splicing mutation in ELAC2 suggests phenotypic variability including intellectual disability with minimal cardiac involvement. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 11(1), 139. doi:10.1186/s13023-016-0526-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

