Acupuncture for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: An Overview of Systematic Reviews
- PMID: 36124104
- PMCID: PMC9482408
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S376759
Acupuncture for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: An Overview of Systematic Reviews
Abstract
Background: Post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) is one of the most common complications after stroke. In recent years, as a complementary alternative therapy, many systematic reviews (SRs) and meta-analysis (MAs) have reported the efficacy and safety of acupuncture in improving cognitive function in patients with PSCI, but the quality of evidence is unknown and therefore needs to be evaluated comprehensively.
Aim: We aimed to evaluate the SRs of acupuncture for patients with PSCI, to summarize the evidence quality of SRs to provide scientific evidence.
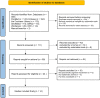
Methods: We searched for relevant SRs and MAs in seven databases up to March 22, 2022. Two reviewers independently completed literature retrieval, screening, and data extraction. We used A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews 2 (AMSTAR 2) to evaluate the methodological quality; the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) tool to determine the strength of evidence; and the ROBIS tool to assess RoB.
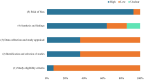
Results: We identified 14 SRs. The methodological quality of all SRs was low (2/14) or very low (12/14). GRADE results showed 13 were moderate quality (26%), 5 were low quality (10%), and 32 were very-low quality (64%). RoB showed that one SR had a low risk and 13 had a high risk. Moderate quality results showed that combined acupuncture therapy was superior to western medicine or cognitive rehabilitation training in improving cognitive function, the total response rate, and the daily living ability of patients with PSCI.
Conclusion: Based on the evidence, acupuncture appears to be effective and safe in improving cognitive function for patients with PSCI, but the overall quality of SRs is not high. High-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture on the cognitive function of patients with PSCI.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO CRD42022315441.
Keywords: AMSTAR-2; GRADE; PSCI; acupuncture; overview.
© 2022 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors stated any conflicts of interest in this study, and there were no potential commercial or financial relationships.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of tongxinluo capsule for angina pectoris of coronary heart disease: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 13;11:1229299. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1229299. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38414926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of multiple acupuncture therapies for post stroke cognitive impairment: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1218095. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1218095. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37638181 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific Evidence of Acupuncture for Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Jul 3;19:1503-1513. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S407162. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 37424960 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of systematic reviews of acupuncture for Parkinson's disease.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 30;18:1415008. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1415008. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39280262 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for treating functional constipation: An overview of systematic reviews.J Integr Med. 2022 Jan;20(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.11.001. Epub 2021 Nov 7. J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 34838459 Review.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture for cognitive impairment after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 May 1;10(9):e30522. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30522. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38765166 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of mental disorders on clinical outcomes of physical diseases: an umbrella review assessing population attributable fraction and generalized impact fraction.World Psychiatry. 2023 Feb;22(1):86-104. doi: 10.1002/wps.21068. World Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36640414 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of combination scalp acupuncture for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2024 Nov 29;18:1468331. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1468331. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39678533 Free PMC article.
-
Global trends and hotspots in research on acupuncture for stroke: a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Sep 21;28(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01253-w. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37735698 Free PMC article.
-
A network meta-analysis of different acupuncture therapy in the treatment of poststroke cognitive impairment and dementia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e40233. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040233. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470518 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials