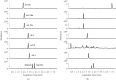
Rapid and Simultaneous Quantification of Six Aristolochic Acids and Two Lignans in Asari Radix et Rhizoma Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 36124165
- PMCID: PMC9482547
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5269545
Rapid and Simultaneous Quantification of Six Aristolochic Acids and Two Lignans in Asari Radix et Rhizoma Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
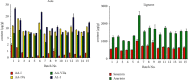
Asari Radix et Rhizoma (AR) is a widely-used Chinese herbal medicine containing multiple active lignans and rare nephrotoxic components-aristolochic acids derivatives (AAs). However, the current quality control method carried out by Chinese Pharmacopoeia has defects in trace AAs detection and insufficient marker ingredients, which is unable to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy and safety of AR. To improve the quality control method of AR, a rapid, sensitive, and reliable chromatographic analytic method based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QqQ-MS) was established for the simultaneous analysis of multiple AAs and lignans in AR samples. Positive electrospray ionization mode with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) was applied for the detection of the eight analytes. The method showed available linearity (R 2 ≥ 0.991), the limit of quantification (2-5 ng/mL), precision (RSD <8.12%), and accuracy (89.78-112.16%). A total of 6 AAs and 2 lignans were quantified for their content in 15 AR samples. The content of AA-IVa, AA-VIIa, and aristololactam I (AL-I) was much higher than the AA-I controlled by pharmacopoeia. Considering the potential toxicity of AAs, AA-IVa, AA-VIIa, and AL-I should also be controlled in AR. A considerable amount of active sesamin was detected in AR, suggesting that it could be added as a quality marker for the quality control of AR. The newly developed analytical method could be applied for the fast evaluation of toxic AA's content and quality during quality control of AR or preparations containing AR.
Copyright © 2022 Hanze Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous determination of twenty-two components in Asari Radix et Rhizoma by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Planta Med. 2014 Dec;80(18):1753-62. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1383296. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Planta Med. 2014. PMID: 25513865
-
Comparative analysis of multiple representative components in the herb pair Astragali Radix-Curcumae Rhizoma and its single herbs by UPLC-QQQ-MS.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jan 30;148:224-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.09.015. Epub 2017 Oct 14. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29055246
-
Discovery of chemical markers for identifying species, growth mode and production area of Astragali Radix by using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry.Phytomedicine. 2020 Feb;67:153155. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153155. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 31901890
-
Two-dimensional liquid chromatography based on different modulations for the determination of Aristolochic Acid Ⅰ in Asari Radix et Rhizoma.J Chromatogr A. 2025 Jan 11;1740:465573. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465573. Epub 2024 Dec 1. J Chromatogr A. 2025. PMID: 39637614
-
Recent developments in detoxication techniques for aristolochic acid-containing traditional Chinese medicines.RSC Adv. 2020 Jan 8;10(3):1410-1425. doi: 10.1039/c9ra08327h. eCollection 2020 Jan 7. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35494720 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Dec 22;29(1):81. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010081. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Committee of National Pharmacopoeia. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China . Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2020.
-
- Kim E. J., Chen Y., Huang J. Q., et al. Evidence-based toxicity evaluation and scheduling of Chinese herbal medicines. Journal of Ethnopharmacology . 2013;146(1):40–61. - PubMed
-
- Cosyns J. P. Aristolochic acid and ‘Chinese herbs nephropathy’: a review of the evidence to date. Drug Safety . 2003;26(1):33–48. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Z. B., Jiang W. Y., Cai S. Q. Clinical and pharmaceutical development and its thought of Chinese herbal nephropathy induced by aristolochic acid. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs . 2003;34(2):93–96.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials