Efficacy and safety of intravitreal HLX04-O, an anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 36124180
- PMCID: PMC9453407
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.09.20
Efficacy and safety of intravitreal HLX04-O, an anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of HLX04-O, an investigational ophthalmic formulation of HLX04 (bevacizumab biosimilar) for intravitreal injection, as a treatment for wet age-related macular degeneration (wAMD) in a phase 1/2 clinical trial (NCT04993352).
Methods: Eligible patients with wAMD were enrolled to receive HLX04-O intravitreal injections at a dose of 1.25 mg/0.05 mL every four weeks. Efficacy and adverse events were evaluated every month during study visits.
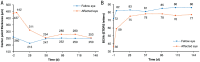
Results: A 76-year-old male with wAMD in his left eye participated in the trial and completed six cycles of HLX04-O intravitreal injections. Changes were observed in macular center point thickness (baseline vs last study visit, 437 vs 255 µm) and best-corrected visual acuity letter score (baseline vs last study visit, 36 vs 77) of the affected eye, which indicated an improvement in wAMD over treatment. No adverse events were reported by the data cutoff date.
Conclusion: HLX04-O at 1.25 mg/0.05 mL every four weeks is well tolerated in this patient, demonstrating promising safety and efficacy in wAMD treatment. Large-scale studies are required to confirm the outcomes.
Keywords: HLX04; HLX04-O; anti-vascular endothelial growth factor; bevacizumab; wet age-related macular degeneration.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy, Safety, and Immunogenicity of HLX04 Versus Reference Bevacizumab in Combination with XELOX or mFOLFOX6 as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind Phase III Study.BioDrugs. 2021 Jul;35(4):445-458. doi: 10.1007/s40259-021-00484-9. Epub 2021 May 20. BioDrugs. 2021. PMID: 34014555 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
TEN-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF PATIENTS WITH EXUDATIVE AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION TREATED WITH INTRAVITREAL ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR INJECTIONS.Retina. 2020 Sep;40(9):1665-1672. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002668. Retina. 2020. PMID: 31725524
-
Long-term effects of intravitreal bevacizumab and aflibercept on intraocular pressure in wet age-related macular degeneration.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Aug 28;21(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02076-1. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34454473 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for macular oedema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 7;7(7):CD009510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32633861 Free PMC article.
-
Different antivascular endothelial growth factor treatments and regimens and their outcomes in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a literature review.Br J Ophthalmol. 2013 Dec;97(12):1497-507. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-303394. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23929309 Review.
Cited by
-
Ocular Delivery of Therapeutic Agents by Cell-Penetrating Peptides.Cells. 2023 Apr 1;12(7):1071. doi: 10.3390/cells12071071. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mitchell P, Liew G, Gopinath B, Wong TY. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet. 2018;392(10153):1147–1159. - PubMed
-
- Wong WL, Su XY, Li X, Cheung CMG, Klein R, Cheng CY, Wong TY. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(2):e106–e116. - PubMed
-
- de Jong EK, Geerlings MJ, den Hollander AI. Genetics and Genomics of Eye Disease. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2020. Age-related macular degeneration; pp. 155–180.
-
- Henlius' 4th Biologics: Bevacizumab Biosimilar Han-Bei-Tai® Approved by National Medical Products Administration. [Accessed on December 3, 2021]. https://www.henlius.com/en/NewsDetails-3329-26.html.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
