Corneal histomorphology and electron microscopic observation of R124L mutated corneal dystrophy in a relapsed pedigree
- PMID: 36124191
- PMCID: PMC9453408
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.09.02
Corneal histomorphology and electron microscopic observation of R124L mutated corneal dystrophy in a relapsed pedigree
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the histological characteristics and ultrastructure of recurrent Chinese R124L mutated corneal dystrophy after keratoplasty.
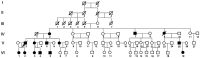
Methods: The subjects were enrolled from a Chinese family of corneal dystrophy with R124L heterozygous gene mutation and with a history of consanguineous marriage. Normal corneal samples were used as controls.
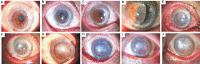
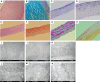
Results: In this family, 2 patients (3 eyes) underwent penetrating keratoplasty (PKP) and 2 patients (4 eyes) underwent lamellar keratoplasty (LKP). They had recurrence at 33.5±3.0 (range 30-36)mo after keratoplasty. Among them, 1 patient (1 eye) underwent PKP again and 1 patient (2 eyes) underwent LKP again. In the R124L mutated recurrent corneal dystrophy, the corneal turbidity was mainly distributed from the upper corneal cortex to the anterior stroma; the corneal epithelium surface was rougher and more uneven; and, the corneal erosions were larger. Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that the thickness of the corneal epithelium was uneven; the arrangement of the epithelial cells was disordered; and, some corneal epithelial cells were swollen. The results of Congo red staining, Masson's trichrome staining and Periodic acid-Schiff staining were positive, while that of Alcian blue staining was negative. Under a transmission electron microscope, deposition of high electron density substances between epithelial and basal cells, and, apoptosis of basal cells were observed. Many high electron density depositions were observed in the sub-epithelial and anterior corneal matrix.
Conclusion: In the Chinese family of recurrent corneal dystrophy with R124L gene mutation, the corneal epithelia of the recurrent cases are rougher, and the corneal depositions are extracellular amyloid fibrin.
Keywords: R124L mutation; corneal dystrophy; electron microscope observation; pathology.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The observation of anterior segment in children with an R124L mutation corneal dystrophy by anterior segment optical coherence tomography and in vivo confocal microscopy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 28;9:991204. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.991204. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36388887 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mutation at codon 124 (R124L) in the BIGH3 gene is associated with a superficial variant of granular corneal dystrophy.Arch Ophthalmol. 1999 Jan;117(1):90-3. doi: 10.1001/archopht.117.1.90. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999. PMID: 9930165
-
A corneal dystrophy associated with transforming growth factor beta-induced Gly623Asp mutation an amyloidogenic phenotype.Ophthalmology. 2009 Jan;116(1):46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.08.050. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Ophthalmology. 2009. PMID: 19019446
-
Recurrent Meesmann's corneal epithelial dystrophy after penetrating keratoplasty.Cornea. 1998 Sep;17(5):566-70. doi: 10.1097/00003226-199809000-00017. Cornea. 1998. PMID: 9756454
-
Stage-related therapy of corneal dystrophies.Dev Ophthalmol. 2011;48:116-153. doi: 10.1159/000324081. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Dev Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21540634 Review.
References
-
- Atia R, Jouve L, Georgon C, Laroche L, Borderie V, Bouheraoua N. Imaging of reis-Bückler corneal dystrophy. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019;42(1):105–107. - PubMed
-
- Moshirfar M, Bennett P, Ronquillo Y. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Corneal Dystrophy. - PubMed
-
- Cai JQ, Zhu LR, Zha Y, Kang QY. TGFBI gene mutation analysis in Chinese families with corneal dystrophies. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016;20(7):388–392. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YL, Ying JL, Zhou WP, Zhu LR, Cai JQ. Analyses of TGFBI gene mutation spectrum in four Chinese families with corneal dystrophy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;95(2):116–119. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
