Deletion of mdig enhances H3K36me3 and metastatic potential of the triple negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 36124233
- PMCID: PMC9482110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105057
Deletion of mdig enhances H3K36me3 and metastatic potential of the triple negative breast cancer cells
Abstract
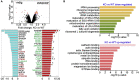
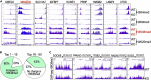
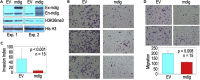
In this report, we provide evidence showing diminished expression of the mineral dust-induced gene (mdig), a previously identified oncogenic gene, in human triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Using a mouse model of orthotopic xenograft of the TNBC MDA-MB-231 cells, we demonstrate that mdig promotes the growth of primary tumors but inhibits metastasis of these cells in vivo. Knockout of mdig resulted in an enhancement of H3K36me3 in the genome and upregulation of some X chromosome-linked genes for cell motility, invasion, and metastasis. Silencing MAGED2, one of the most upregulated and H3K36me3-enriched genes resulted from mdig depletion, can partially reverse the invasive migration of the mdig knockout cells. The anti-metastatic and inhibitory role of mdig on H3K36me3 was cross-validated in another cell line, A549 lung cancer cells. Together, our data suggest that mdig is antagonist against H3K36me3 that enforces expression of genes, such as MAGED2, for cell invasion and metastasis.
Keywords: Cancer; Molecular biology; Molecular mechanism of gene regulation.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Bi Z., Zhang Q., Fu Y., Seno A., Wadgaonkar P., Qiu Y., Almutairy B., Xu L., Zhang W., Thakur C., Chen F. Cooperation between NRF2-mediated transcription and MDIG-dependent epigenetic modifications in arsenic-induced carcinogenesis and cancer stem cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021;76:310–318. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birkbak N.J., McGranahan N. Cancer genome evolutionary trajectories in metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:8–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

