The effects of secondary bacterial metabolites on photosynthesis in microalgae cells
- PMID: 36124259
- PMCID: PMC9481811
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-022-00981-3
The effects of secondary bacterial metabolites on photosynthesis in microalgae cells
Abstract
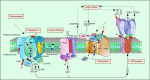
Secondary metabolites of bacteria are regulatory molecules that act as "info-chemicals" that control some metabolic processes in the cells of microorganisms. These molecules provide the function of bacteria communication in microbial communities. As primary producers of organic matter in the biosphere, microalgae play a central ecological role in various ecosystems. Photosynthesis is a central process in microalgae cells, and it is exposed to various biotic and abiotic factors. Various secondary metabolites of bacteria confer a noticeable regulatory effect on photosynthesis in microalgae cells. The main purpose of this review is to highlight recent experimental results that demonstrate the impact of several types of common bacterial metabolites (volatile organic compounds, non-protein amino acids, and peptides) on photosynthetic activity in cells of microalgae. The use of these molecules as herbicides can be of great importance both for practical applications and for basic research.
Keywords: Allelopathic molecules; BMAA; Chlorophyll; Microcystins; Photosystems; Phytotoxicity; Secondary metabolites; VOCs.
© International Union for Pure and Applied Biophysics (IUPAB) and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Artiga M (2021) Bacterial communication. Biol Philos 36(4). 10.1007/s10539-021-09814-1
-
- Babica P, Bláha L, Maršálek B. Exploring the natural role of microcystins – a review of effects on photoautotrophic organisms. J Phycol. 2006;42:9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00176.x. - DOI
-
- Badger MR, Price GD (2003) CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria: molecular components, their diversity and evolution. J Exp Bot 54:609–622. 10.1093/jxb/erg076 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

