Current state of the primary charge separation mechanism in photosystem I of cyanobacteria
- PMID: 36124265
- PMCID: PMC9481807
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-022-00983-1
Current state of the primary charge separation mechanism in photosystem I of cyanobacteria
Abstract
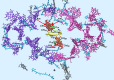
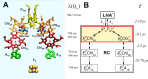
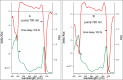
This review analyzes new data on the mechanism of ultrafast reactions of primary charge separation in photosystem I (PS I) of cyanobacteria obtained in the last decade by methods of femtosecond absorption spectroscopy. Cyanobacterial PS I from many species harbours 96 chlorophyll a (Chl a) molecules, including six specialized Chls denoted Chl1A/Chl1B (dimer P700, or PAPB), Chl2A/Chl2B, and Chl3A/Chl3B arranged in two branches, which participate in electron transfer reactions. The current data indicate that the primary charge separation occurs in a symmetric exciplex, where the special pair P700 is electronically coupled to the symmetrically located monomers Chl2A and Chl2B, which can be considered together as a symmetric exciplex Chl2APAPBChl2B with the mixed excited (Chl2APAPBChl2B)* and two charge-transfer states P700 +Chl2A - and P700 +Chl2B -. The redistribution of electrons between the branches in favor of the A-branch occurs after reduction of the Chl2A and Chl2B monomers. The formation of charge-transfer states and the symmetry breaking mechanisms were clarified by measuring the electrochromic Stark shift of β-carotene and the absorption dynamics of PS I complexes with the genetically altered Chl 2B or Chl 2A monomers. The review gives a brief description of the main methods for analyzing data obtained using femtosecond absorption spectroscopy. The energy levels of excited and charge-transfer intermediates arising in the cyanobacterial PS I are critically analyzed.
Keywords: Electron transfer; Femtosecond absorption spectroscopy; Photosystem I; Primary charge separation.
© International Union for Pure and Applied Biophysics (IUPAB) and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
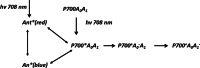


Similar articles
-
Primary charge separation within the structurally symmetric tetrameric Chl2APAPBChl2B chlorophyll exciplex in photosystem I.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021 Apr;217:112154. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112154. Epub 2021 Feb 16. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021. PMID: 33636482
-
Evidence that chlorophyll f functions solely as an antenna pigment in far-red-light photosystem I from Fischerella thermalis PCC 7521.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2020 Jun 1;1861(5-6):148184. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148184. Epub 2020 Mar 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2020. PMID: 32179058
-
Symmetry breaking in photosystem I: ultrafast optical studies of variants near the accessory chlorophylls in the A- and B-branches of electron transfer cofactors.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2021 Sep;20(9):1209-1227. doi: 10.1007/s43630-021-00094-y. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34478050
-
Mechanism of primary and secondary ion-radical pair formation in photosystem I complexes.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2014 Mar;79(3):221-6. doi: 10.1134/S0006297914030079. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2014. PMID: 24821448 Review.
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of primary electron donors in type I photosynthetic reaction centers.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Oct 30;1507(1-3):180-93. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(01)00206-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11687214 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial for the special issue of biophysical reviews on the 9th Congress of the Russian society for photobiology held in Shepsi, Krasnodar region, Russia, on September 12-19, 2021.Biophys Rev. 2022 Aug 17;14(4):743-749. doi: 10.1007/s12551-022-00993-z. eCollection 2022 Aug. Biophys Rev. 2022. PMID: 35990254 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inverted region in the reaction of the quinone reduction in the A1-site of photosystem I from cyanobacteria.Photosynth Res. 2024 Mar;159(2-3):115-131. doi: 10.1007/s11120-023-01020-2. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Photosynth Res. 2024. PMID: 37093503
-
Reversible Photochromic Reactions of Bacteriorhodopsin from Halobacterium salinarum at Femto- and Picosecond Times.Molecules. 2024 Oct 13;29(20):4847. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204847. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459214 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of a photosystem I variant containing an unusual plastoquinone derivative in its electron transfer chain.Sci Adv. 2024 Nov 29;10(48):eadp4937. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp4937. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39612342 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

