Diverse ancestry whole-genome sequencing association study identifies TBX5 and PTK7 as susceptibility genes for posterior urethral valves
- PMID: 36124557
- PMCID: PMC9512401
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.74777
Diverse ancestry whole-genome sequencing association study identifies TBX5 and PTK7 as susceptibility genes for posterior urethral valves
Abstract
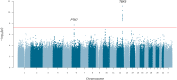
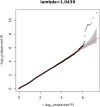
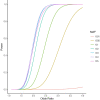
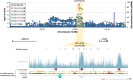
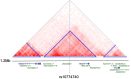
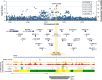
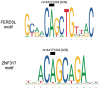
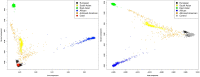
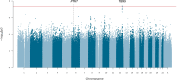
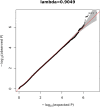
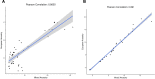
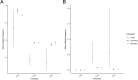
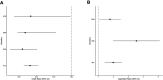
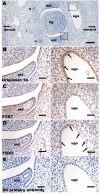
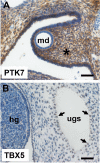
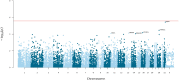
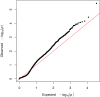
Posterior urethral valves (PUV) are the commonest cause of end-stage renal disease in children, but the genetic architecture of this rare disorder remains unknown. We performed a sequencing-based genome-wide association study (seqGWAS) in 132 unrelated male PUV cases and 23,727 controls of diverse ancestry, identifying statistically significant associations with common variants at 12q24.21 (p=7.8 × 10-12; OR 0.4) and rare variants at 6p21.1 (p=2.0 × 10-8; OR 7.2), that were replicated in an independent European cohort of 395 cases and 4151 controls. Fine mapping and functional genomic data mapped these loci to the transcription factor TBX5 and planar cell polarity gene PTK7, respectively, the encoded proteins of which were detected in the developing urinary tract of human embryos. We also observed enrichment of rare structural variation intersecting with candidate cis-regulatory elements, particularly inversions predicted to affect chromatin looping (p=3.1 × 10-5). These findings represent the first robust genetic associations of PUV, providing novel insights into the underlying biology of this poorly understood disorder and demonstrate how a diverse ancestry seqGWAS can be used for disease locus discovery in a rare disease.
Keywords: CAKUT; PUV; developmental biology; genetics; genome-wide association study; genomics; human; posterior urethral valves; seqGWAS; whole-genome sequencing.
© 2022, Chan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MC, OS, FL, AH, HS, CV, GB, WN, MZ, SW, YH, JC, DW, CM, AS, AK, RK, AW, DB, AL, DG No competing interests declared
Figures


References
-
- Basson CT, Bachinsky DR, Lin RC, Levi T, Elkins JA, Soults J, Grayzel D, Kroumpouzou E, Traill TA, Leblanc-Straceski J, Renault B, Kucherlapati R, Seidman JG, Seidman CE. Mutations in human tbx5 [corrected] cause limb and cardiac malformation in holt-oram syndrome. Nature Genetics. 1997;15:30–35. doi: 10.1038/ng0197-30. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berndt SI, Wang Z, Yeager M, Alavanja MC, Albanes D, Amundadottir L, Andriole G, Beane Freeman L, Campa D, Cancel-Tassin G, Canzian F, Cornu JN, Cussenot O, Diver WR, Gapstur SM, Grönberg H, Haiman CA, Henderson B, Hutchinson A, Hunter DJ, Key TJ, Kolb S, Koutros S, Kraft P, Le Marchand L, Lindström S, Machiela MJ, Ostrander EA, Riboli E, Schumacher F, Siddiq A, Stanford JL, Stevens VL, Travis RC, Tsilidis KK, Virtamo J, Weinstein S, Wilkund F, Xu J, Lilly Zheng S, Yu K, Wheeler W, Zhang H, Sampson J, Black A, Jacobs K, Hoover RN, Tucker M, Chanock SJ, African Ancestry Prostate Cancer GWAS Consortium Two susceptibility loci identified for prostate cancer aggressiveness. Nature Communications. 2015;6:6889. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7889. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boghossian NS, Sicko RJ, Kay DM, Rigler SL, Caggana M, Tsai MY, Yeung EH, Pankratz N, Cole BR, Druschel CM, Romitti PA, Browne ML, Fan R, Liu A, Brody LC, Mills JL. Rare copy number variants implicated in posterior urethral valves. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A. 2016;170:622–633. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37493. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

