High-level gonosomal mosaicism for a pathogenic non-coding CNV deletion of the lung-specific FOXF1 enhancer in an unaffected mother of an infant with ACDMPV
- PMID: 36124617
- PMCID: PMC9651602
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.2062
High-level gonosomal mosaicism for a pathogenic non-coding CNV deletion of the lung-specific FOXF1 enhancer in an unaffected mother of an infant with ACDMPV
Abstract
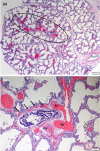
Background: Alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins (ACDMPV) results from haploinsufficiency of the mesenchymal transcription factor FOXF1 gene. To date, only one case of an ACDMPV-causative CNV deletion inherited from a very-low level somatic mosaic mother has been reported.
Methods: Clinical, histopathological, and molecular studies, including whole genome sequencing, chromosomal microarray analysis, qPCR, and Sanger sequencing, followed by in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) were used to study a family with a deceased neonate with ACDMPV.
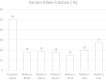
Results: A pathogenic CNV deletion of the lung-specific FOXF1 enhancer in the proband was found to be inherited from an unaffected mother, 36% mosaic for this deletion in her peripheral blood cells. The qPCR analyses of saliva, buccal cells, urine, nail, and hair samples revealed 19%, 18%, 15%, 19%, and 27% variant allele fraction, respectively, indicating a high recurrence risk. Grandparental studies revealed that the deletion arose on the mother's paternal chromosome 16. PGT studies revealed 44% embryos with the deletion, reflecting high-level germline mosaicism.
Conclusion: Our data further demonstrate the importance of parental testing in ACDMPV families and reproductive usefulness of IVF with PGT in families with high-level parental gonosomal mosaicism.
Keywords: genetics of lung development; germline mosaicism; parental mosaicism; somatic mosaicism.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of rare non-coding SNVs in the lung-specific FOXF1 enhancer with a mitigation of the lethal ACDMPV phenotype.Hum Genet. 2019 Dec;138(11-12):1301-1311. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02073-x. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31686214 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenetics of alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins.Hum Genet. 2016 May;135(5):569-586. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1655-9. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27071622 Free PMC article.
-
Novel FOXF1 deep intronic deletion causes lethal lung developmental disorder, alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins.Hum Mutat. 2013 Nov;34(11):1467-71. doi: 10.1002/humu.22395. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Hum Mutat. 2013. PMID: 23943206 Free PMC article.
-
[Alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of the pulmonary veins: a case report and literature review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 2;58(10):838-842. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200427-00441. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32987465 Review. Chinese.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Diseases.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;65(5):473-488. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0152TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34293272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of copy number variations and possible candidate genes in spontaneous abortion by copy number variation sequencing.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 17;14:1218793. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1218793. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37916154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu‐El‐Haija, A. , Fineman, J. , Connolly, A. J. , Murali, P. , Judge, L. M. , & Slavotinek, A. M. (2018). Two patients with FOXF1 mutations with alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins and other malformations: Two different presentations and outcomes. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 176(12), 2877–2881. 10.1002/ajmg.a.40641 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ansari, M. , Poke, G. , Ferry, Q. , Williamson, K. , Aldridge, R. , Meynert, A. M. , Bengani, H. , Chan, C. Y. , Kayserili, H. , Avci, S. , Hennekam, R. C. , Lampe, A. K. , Redeker, E. , Homfray, T. , Ross, A. , Falkenberg Smeland, M. , Mansour, S. , Parker, M. J. , Cook, J. A. , … FitzPatrick, D. (2014). Genetic heterogeneity in Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) and CdLS‐like phenotypes with observed and predicted levels of mosaicism. Journal of Medical Genetics, 51(10), 659–668. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102573 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartnik, M. , Derwinska, K. , Gos, M. , Obersztyn, E. , Kolodziejska, K. E. , Erez, A. , Szpecht‐Potocka, A. , Fang, P. , Terczynska, I. , Mierzewska, H. , Lohr, N. J. , Bellus, G. A. , Reimschisel, T. , Bocian, E. , Mazurczak, T. , Cheung, S. W. , & Stankiewicz, P. (2011). Early‐onset seizures due to mosaic exonic deletions of CDKL5 in a male and two females. Genetics in Medicine, 13(5), 447–452. 10.1097/GIM.0b013e31820605f5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

