EWS/FLI mediated reprogramming of 3D chromatin promotes an altered transcriptional state in Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 36124657
- PMCID: PMC9508825
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac747
EWS/FLI mediated reprogramming of 3D chromatin promotes an altered transcriptional state in Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
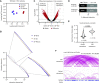
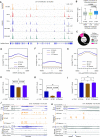
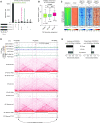
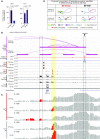
Ewing sarcoma is a prototypical fusion transcription factor-associated pediatric cancer that expresses EWS/FLI or a highly related FET/ETS chimera. EWS/FLI dysregulates transcription to induce and maintain sarcomagenesis, but the mechanisms utilized are not fully understood. We therefore sought to define the global effects of EWS/FLI on chromatin conformation and transcription in Ewing sarcoma cells using a well-validated 'knock-down/rescue' model of EWS/FLI function in combination with next generation sequencing assays to evaluate how the chromatin landscape changes with loss, and recovery, of EWS/FLI expression. We found that EWS/FLI (and EWS/ERG) genomic localization is largely conserved across multiple patient-derived Ewing sarcoma cell lines. This EWS/FLI binding signature is associated with establishment of topologically-associated domain (TAD) boundaries, compartment activation, enhancer-promoter looping that involve both intra- and inter-TAD interactions, and gene activation. In addition, EWS/FLI co-localizes with the loop-extrusion factor cohesin to promote chromatin loops and TAD boundaries. Importantly, local chromatin features provide the basis for transcriptional heterogeneity in regulation of direct EWS/FLI target genes across different Ewing sarcoma cell lines. These data demonstrate a key role of EWS/FLI in mediating genome-wide changes in chromatin configuration and support the notion that fusion transcription factors serve as master regulators of three-dimensional reprogramming of chromatin.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Seth A., Watson D.K.. ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2005; 41:2462–2478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

