The high mobility group protein HMG20A cooperates with the histone reader PHF14 to modulate TGFβ and Hippo pathways
- PMID: 36124662
- PMCID: PMC9508832
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac766
The high mobility group protein HMG20A cooperates with the histone reader PHF14 to modulate TGFβ and Hippo pathways
Abstract
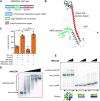
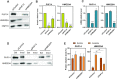
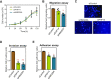
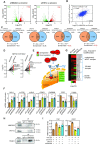
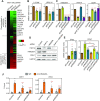
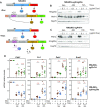
High mobility group (HMG) proteins are chromatin regulators with essential functions in development, cell differentiation and cell proliferation. The protein HMG20A is predicted by the AlphaFold2 software to contain three distinct structural elements, which we have functionally characterized: i) an amino-terminal, intrinsically disordered domain with transactivation activity; ii) an HMG box with higher binding affinity for double-stranded, four-way-junction DNA than for linear DNA; and iii) a long coiled-coil domain. Our proteomic study followed by a deletion analysis and structural modeling demonstrates that HMG20A forms a complex with the histone reader PHF14, via the establishment of a two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coil structure. siRNA-mediated knockdown of either PHF14 or HMG20A in MDA-MB-231 cells causes similar defects in cell migration, invasion and homotypic cell-cell adhesion ability, but neither affects proliferation. Transcriptomic analyses demonstrate that PHF14 and HMG20A share a large subset of targets. We show that the PHF14-HMG20A complex modulates the Hippo pathway through a direct interaction with the TEAD1 transcription factor. PHF14 or HMG20A deficiency increases epithelial markers, including E-cadherin and the epithelial master regulator TP63 and impaired normal TGFβ-trigged epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Taken together, these data indicate that PHF14 and HMG20A cooperate in regulating several pathways involved in epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Wynder C., Hakimi M.A., Epstein J.A., Shilatifard A., Shiekhattar R.. Recruitment of MLL by HMG-domain protein iBRAF promotes neural differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005; 7:1113–1117. - PubMed
-
- Lee M.G., Wynder C., Cooch N., Shiekhattar R.. An essential role for CoREST in nucleosomal histone 3 lysine 4 demethylation. Nature. 2005; 437:432–435. - PubMed
-
- Rivero S., Ceballos-Chavez M., Bhattacharya S.S., Reyes J.C.. HMG20A is required for SNAI1-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 2015; 34:5264–5276. - PubMed
-
- Ceballos-Chavez M., Rivero S., Garcia-Gutierrez P., Rodriguez-Paredes M., Garcia-Dominguez M., Bhattacharya S., Reyes J.C.. Control of neuronal differentiation by sumoylation of BRAF35, a subunit of the LSD1-CoREST histone demethylase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012; 109:8085–8090. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

