Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Elevated PTH Levels Among the US General Population
- PMID: 36125184
- PMCID: PMC9693802
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgac544
Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Elevated PTH Levels Among the US General Population
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Elevated PTH Levels Among the US General Population".J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jan 17;108(2):e29. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac676. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36451340 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Context: Although elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels are associated with higher mortality risks, the evidence is limited as to when PTH is expected to be elevated and thus should be measured among the general population.
Objective: This work aimed to build a machine learning-based prediction model of elevated PTH levels based on demographic, lifestyle, and biochemical data among US adults.
Methods: This population-based study included adults aged 20 years or older with a measurement of serum intact PTH from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003 to 2006. We used the NHANES 2003 to 2004 cohort (n = 4096) to train 6 machine-learning prediction models (logistic regression with and without splines, lasso regression, random forest, gradient-boosting machines [GBMs], and SuperLearner). Then, we used the NHANES 2005 to 2006 cohort (n = 4112) to evaluate the model performance including area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
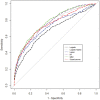
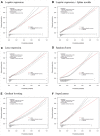
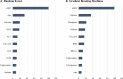
Results: Of 8208 US adults, 753 (9.2%) showed PTH greater than 74 pg/mL. Across 6 algorithms, the highest AUC was observed among random forest (AUC [95% CI] = 0.79 [0.76-0.81]), GBM (AUC [95% CI] = 0.78 [0.75-0.81]), and SuperLearner (AUC [95% CI] = 0.79 [0.76-0.81]). The AUC improved from 0.69 to 0.77 when we added cubic splines for the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in the logistic regression models. Logistic regression models with splines showed the best calibration performance (calibration slope [95% CI] = 0.96 [0.86-1.06]), while other algorithms were less calibrated. Among all covariates included, eGFR was the most important predictor of the random forest model and GBM.
Conclusion: In this nationally representative data in the United States, we developed a prediction model that potentially helps us to make accurate and early detection of elevated PTH in general clinical practice. Future studies are warranted to assess whether this prediction tool for elevated PTH would improve adverse health outcomes.
Keywords: NHANES; hyperparathyroidism; machine learning; parathyroid hormone; prediction model.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Fraser WD. Hyperparathyroidism. Lancet. 2009;374(9684):145–158. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JL, Vanwoerkom RC, Horne BD, et al. . Parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, renal dysfunction, and cardiovascular disease: dependent or independent risk factors? Am Heart J. 2011;162(2):331–339.e2. - PubMed
-
- Domiciano DS, Machado LG, Lopes JB, et al. . Bone mineral density and parathyroid hormone as independent risk factors for mortality in community-dwelling older adults: a population-based prospective cohort study in Brazil. The São Paulo Ageing & Health (SPAH) Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(6):1146–1157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

