A 29-MRNA HOST RESPONSE WHOLE-BLOOD SIGNATURE IMPROVES PREDICTION OF 28-DAY MORTALITY AND 7-DAY INTENSIVE CARE UNIT CARE IN ADULTS PRESENTING TO THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT WITH SUSPECTED ACUTE INFECTION AND/OR SEPSIS
- PMID: 36125356
- PMCID: PMC9512237
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001970
A 29-MRNA HOST RESPONSE WHOLE-BLOOD SIGNATURE IMPROVES PREDICTION OF 28-DAY MORTALITY AND 7-DAY INTENSIVE CARE UNIT CARE IN ADULTS PRESENTING TO THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT WITH SUSPECTED ACUTE INFECTION AND/OR SEPSIS
Abstract
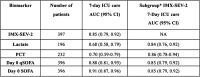
Background: Risk stratification of emergency department patients with suspected acute infections and/or suspected sepsis remains challenging. We prospectively validated a 29-messenger RNA host response classifier for predicting severity in these patients. Methods: We enrolled adults presenting with suspected acute infections and at least one vital sign abnormality to six emergency departments in Greece. Twenty-nine target host RNAs were quantified on NanoString nCounter and analyzed with the Inflammatix Severity 2 (IMX-SEV-2) classifier to determine risk scores as low, moderate, and high severity. Performance of IMX-SEV-2 for prediction of 28-day mortality was compared with that of lactate, procalcitonin, and quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA). Results: A total of 397 individuals were enrolled; 38 individuals (9.6%) died within 28 days. Inflammatix Severity 2 classifier predicted 28-day mortality with an area under the receiver operator characteristics curve of 0.82 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.74-0.90) compared with lactate, 0.66 (95% CI, 0.54-0.77); procalcitonin, 0.67 (95% CI, 0.57-0.78); and qSOFA, 0.81 (95% CI, 0.72-0.89). Combining qSOFA with IMX-SEV-2 improved prognostic accuracy from 0.81 to 0.89 (95% CI, 0.82-0.96). The high-severity (rule-in) interpretation band of IMX-SEV-2 demonstrated 96.9% specificity for predicting 28-day mortality, whereas the low-severity (rule-out) band had a sensitivity of 78.9%. Similarly, IMX-SEV-2 alone accurately predicted the need for day-7 intensive care unit care and further boosted overall accuracy when combined with qSOFA. Conclusions: Inflammatix Severity 2 classifier predicted 28-day mortality and 7-day intensive care unit care with high accuracy and boosted the accuracy of clinical scores when used in combination.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00329582.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Shock Society.
Conflict of interest statement
James W. Wacker, Florian Uhle, Oliver Liesenfeld, and Timothy E. Sweeney are employees and stock option holders of Inflammatix Inc. Catherine A. Hogan is a consultant for Inflammatix. E.J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis has received honoraria from Abbott CH, InflaRx GmbH, MSD Greece, XBiotech Inc., and B·R·A·H·M·S GmbH (Thermo Fisher Scientific); independent educational grants from AbbVie Inc., Abbott CH, bioMérieux Inc., Novartis, InflaRx GmbH, UCB, Sobi, and XBiotech Inc; and funding from the Horizon2020 Marie-Curie Project European Sepsis Academy (granted to the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens), the Horizon 2020 European Grants ImmunoSep and RISKinCOVID (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis), and by the Horizon Europe grant EPIC-CROWN-2 (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis). The other authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Figures