A Systematic Review on Whether an Association Exists Between Adolescent Obesity and Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
- PMID: 36127965
- PMCID: PMC9477550
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.28071
A Systematic Review on Whether an Association Exists Between Adolescent Obesity and Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Abstract
Pseudotumor cerebri syndrome (PTCS)/idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a clinical presentation appertaining to signs/symptoms of raised intracranial pressure, like headache and papilledema. It is an uncommon but clinically significant cause of morbidity such as permanent vision loss. It is crucial to understand if idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is on the rise in adolescents, it is probably due to the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. Our study aimed to find an association between obesity and IIH in adolescents. We utilized Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis 2020 (PRISMA) guidelines to run this systematic review. Many publications related to the topic in the discussion were scrutinized through a comprehensive database search. We filtered them down to a final count of 10 articles after utilizing our inclusion/exclusion criteria and assessing the quality of work. In these final papers, we identified several possibilities to explain the link between obesity and IIH in adolescents. Overweight and obese adolescents were found to have a significantly increased risk of IIH development, with a more severe clinical picture seen in morbidly obese female patients.
Keywords: adolescent obesity; headache; idiopathic intracranial hypertension; lumbar puncture; obesity; overweight; papilledema; pseudotumor cerebri; ptcs; vision loss.
Copyright © 2022, Zafar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

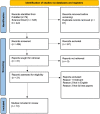

References
-
- Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Neurology. 2013;81:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Symptoms and disease associations in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri): a case-control study. Giuseffi V, Wall M, Siegel PZ, Rojas PB. Neurology. 1991;41:239–244. - PubMed
-
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in children: the Iowa experience. Babikian P, Corbett J, Bell W. J Child Neurol. 1994;9:144–149. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
