Therapeutic strategy of severe circular calcified carotid plaque with hemodynamic impairment: A patient treated by carotid endarterectomy following balloon angioplasty to prevent hyperperfusion
- PMID: 36128112
- PMCID: PMC9479608
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_417_2022
Therapeutic strategy of severe circular calcified carotid plaque with hemodynamic impairment: A patient treated by carotid endarterectomy following balloon angioplasty to prevent hyperperfusion
Abstract
Background: Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome (HPS) is a serious complication. Recently, staged angioplasty has been reported as an effective strategy to avoid HPS. Severe calcification has been reported as contraindication of carotid artery stenting (CAS). In these cases, carotid endarterectomy (CEA) might be an alternative second stage treatment. We present a case of severe circular calcified plaque with hemodynamic impairments, treated with CEA following percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) to prevent HPS.
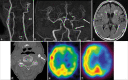
Case description: A 77-year-old woman presented with severe stenosis at the proximal left internal carotid artery. A CT scan of the neck demonstrated circular calcification. 123I-iodoamphetamine single-photon emission computed tomography (123I-IMP SPECT) showed reductions in cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral vascular reserve in the left hemisphere. Staged therapy was subsequently performed as this patient had a high risk of HPS after conventional CAS or CEA. In the first stage, PTA was performed under local anesthesia. Two days after the procedure, 123I-IMP SPECT revealed improvements in CBF. There were no neurological morbidities. CEA was then performed under general anesthesia 7 days later, for the second stage. We found a calcified plaque with a large thrombus at its proximal end. A hematoxylin-eosin stain of the thrombus showed mostly intact and partially lytic blood cells. Postoperative 123I-IMP SPECT revealed CBF was improved, with no hyperperfusion immediately and 2 days after CEA. The patient was discharged with no neurological deficits.
Conclusion: CEA following PTA for severe circular calcified plaque can be an alternative treatment strategy to prevent HPS. A disadvantage is the formation of thrombi. Early CEA should be considered if thrombus formation is suspected.
Keywords: Calcified plaque; Carotid endarterectomy; Hyperperfusion; Staged angioplasty.
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Staged carotid artery angioplasty and stenting for patients with high-grade carotid stenosis with high risk of developing hyperperfusion injury: a retrospective analysis of 44 cases.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2016 Dec 19;1(4):147-153. doi: 10.1136/svn-2016-000024. eCollection 2016 Dec. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2016. PMID: 28959477 Free PMC article.
-
Epileptic seizures attributed to cerebral hyperperfusion after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting of the internal carotid artery.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2000 Sep-Oct;10(5):374-9. doi: 10.1159/000016093. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2000. PMID: 10971023
-
Does preoperative measurement of cerebral blood flow with acetazolamide challenge in addition to preoperative measurement of cerebral blood flow at the resting state increase the predictive accuracy of development of cerebral hyperperfusion after carotid endarterectomy? Results from 500 cases with brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography study.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015;55(2):141-8. doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2014-0269. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 25746308 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Severe Bilateral Symptomatic Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis: Case Report and Literature Review.J Pers Med. 2024 Aug 23;14(9):893. doi: 10.3390/jpm14090893. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39338147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting: the quest continues.Am J Surg. 2008 Feb;195(2):259-69. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.07.022. Am J Surg. 2008. PMID: 18154764 Review.
References
-
- Chang CK, Huded CP, Nolan BW, Powell RJ. Prevalence and clinical significance of stent fracture and deformation following carotid artery stenting. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:685–90. - PubMed
-
- Clark DJ, Lessio S, O’Donoghue M, Schainfeld R, Rosenfield K. Safety and utility of intravascular ultrasound-guided carotid artery stenting. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2004;63:355–62. - PubMed
-
- Derdeyn CP, Videen TO, Yundt KD, Fritsch SM, Carpenter DA, Grubb RL, et al. Variability of cerebral blood volume and oxygen extraction: Stages of cerebral haemodynamic impairment revisited. Brain. 2002;125:595–607. - PubMed
-
- Egashira Y, Yoshimura S, Yamada K, Enomoto Y, Asano T, Iwama T. Stepwise revascularization by carotid endarterectomy after balloon angioplasty for symptomatic severe carotid artery stenosis. Ann Vasc Surg. 2012;26:13.e9–13. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
