Therapeutic Maintenance Level of Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A RBSMR Study
- PMID: 36128204
- PMCID: PMC9450203
- DOI: 10.31138/mjr.33.2.224
Therapeutic Maintenance Level of Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A RBSMR Study
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to determine the therapeutic maintenance level of methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis patients enrolled in the Moroccan biotherapy registry and to identify predictive factors for discontinuing MTX treatment.
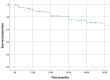
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using the baseline data of the Moroccan biotherapy registry for RBSMR (a multicentric study that aims to evaluate tolerance of biological therapy on patients affected with rheumatic diseases). Demographics and disease features were compared using descriptive statistics. Therapeutic maintenance levels were determined according to a Kaplan-Meier survival curve and a univariate Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to compare the strength of potential factors, followed by a multivariate Cox model to identify significant predictors of MTX discontinuation. Statistically significant results were considered for p values less than 0.05.
Results: 224 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were included in this study. The mean age of patients was 51.83±11.26 years with a majority of females (87.50%). The median duration of disease was 12 [1.66-41.02] years. The therapeutic maintenance level of MTX was 91.1% at 1 year, 87.1% at 2 years, and 68.3% at 5 years. The median of treatment duration was 2, 02 [0, 46-27,76] years. Causes of treatment interruption were side effects (66/88=75%), inefficiency (12/88=13.63%), and other reasons (10/88=11.36%). Predictive factors for stopping MTX were presence of rheumatoid factor (HR 2.24; 95% CI 1.14-5.15; p=0.02) and the access to education (HR 0.37; 95% CI 0.16-0.88; p=0.02).
Conclusion: The therapeutic maintenance level of MTX in our study was satisfactory and comparable to other series, and influenced by many factors such as the occurrence of a side effect. It is necessary to sensitise medical practitioners on symptomatic prevention and management of side effects.
Keywords: Morocco; biotherapy registry; methotrexate; rheumatoid arthritis; rheumatology; therapeutic.
© 2022 The Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology (MJR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Symmons DP, Jones MA, Scott DL, Prior P. Long term mortality outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: early presenters continue to do well. J Rheumatol 1998;25:1072–7. - PubMed
-
- Daien C, Hua C, Gaujoux-Viala C, Cantagrel A, Dubremetz M, Dougados M, et al. Update of French society for rheumatology recommendations for managing rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 2019;135–50. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:960–77. - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Gibson K A, Isabel C. Update on Methotrexate as the Anchor Drug for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 2013; 71 Suppl 1:S9–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources