OligoTRAFTACs: A generalizable method for transcription factor degradation
- PMID: 36128504
- PMCID: PMC9428672
- DOI: 10.1039/d2cb00138a
OligoTRAFTACs: A generalizable method for transcription factor degradation
Abstract
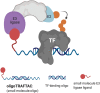
Dysregulated transcription factors (TFs) that rewire gene expression circuitry are frequently identified as key players in disease. Although several TFs have been drugged with small molecules, the majority of oncogenic TFs are not currently pharmaceutically tractable due to their paucity of ligandable pockets. The first generation of transcription factor targeting chimeras (TRAFTACs) was developed to target TFs for proteasomal degradation by exploiting their DNA binding ability. In the current study, we have developed the second generation TRAFTACs ("oligoTRAFTACs") composed of a TF-binding oligonucleotide and an E3 ligase-recruiting ligand. Herein, we demonstrate the development of oligoTRAFTACs to induce the degradation of two oncogenic TFs, c-Myc and brachyury. In addition, we show that brachyury can be successfully degraded by oligoTRAFTACs in chordoma cell lines. Furthermore, zebrafish experiments demonstrate in vivo oligoTRAFTAC activity. Overall, our data demonstrate oligoTRAFTACs as a generalizable platform towards difficult-to-drug TFs and their degradability via the proteasomal pathway.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
C. M. C is founder, shareholder, and consultant to Arvinas, Inc. and Halda, LLC, which support research in his laboratory.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeted degradation of transcription factors by TRAFTACs: TRAnscription Factor TArgeting Chimeras.Cell Chem Biol. 2021 May 20;28(5):648-661.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Cell Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33836141 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical E3 ligase ZFP91 promotes small-molecule-induced E2F2 transcription factor degradation for cancer therapy.EBioMedicine. 2022 Dec;86:104353. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104353. Epub 2022 Nov 11. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36375317 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel oligonucleotide array-based transcription factor assay platform for genome-wide active transcription factor profiling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Proteome Res. 2008 Mar;7(3):1315-25. doi: 10.1021/pr700642g. Epub 2008 Jan 26. J Proteome Res. 2008. PMID: 18220337
-
Advances in targeting 'undruggable' transcription factors with small molecules.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Sep;20(9):669-688. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00199-0. Epub 2021 May 18. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34006959 Review.
-
Transcription factors in epithelial ovarian cancer: histotype-specific drivers and novel therapeutic targets.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Apr;220:107722. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107722. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33137377 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted protein degradation: advances in drug discovery and clinical practice.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Nov 6;9(1):308. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02004-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39500878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-Based Degraders: From Chemical Biology Tools to Neo-Therapeutics.Chem Rev. 2025 Feb 26;125(4):2120-2183. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00595. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39818743 Review.
-
Nanobody-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (NucleoBodies): The Next Frontier in Oligonucleotide Therapy.Pharm Res. 2025 Feb;42(2):219-236. doi: 10.1007/s11095-025-03829-z. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Pharm Res. 2025. PMID: 39953265 Review.
-
Molecular glues of the regulatory ChREBP/14-3-3 complex protect beta cells from glucolipotoxicity.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 2;16(1):2110. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57241-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40025013 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular glues of the regulatory ChREBP/14-3-3 complex protect beta cells from glucolipotoxicity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 17:2024.02.16.580675. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.16.580675. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 02;16(1):2110. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57241-7. PMID: 38405965 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

