Sudden unexpected death in a 17-year-old boy due to unacknowledged adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 36129618
- PMCID: PMC9490726
- DOI: 10.1007/s12024-022-00525-x
Sudden unexpected death in a 17-year-old boy due to unacknowledged adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
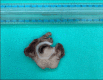
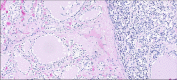
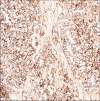
A 17-year-old male with no previous medical history was admitted 2 days before his death to a local hospital after mild dyspnea. Electrocardiography, chest radiography, and blood analysis revealed no abnormalities. Blood oxygen saturation was 99%, and SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs tested negative; thus, he was discharged without prescriptions. After 2 days, the subject died suddenly during a pool party. Forensic autopsy was performed analyzing all anatomical districts. Cardiac causes were fully excluded after deep macroscopic and microscopic evaluation; lung and brain analyses showed no macroscopic pathology. Finally, a large subglottic solid mass was detected. The whitish neoplasm showed an aggressive invasion pattern to the thyroid and adjacent deep soft tissues and occluded the trachea. High-power microscopy showed sheets of small, uniform cells with scant cytoplasm; round nuclei; and small, punctate nucleoli, with immunohistochemical expression of CK8-18, AE1/AE3, and CD99. Using FISH analysis, the break-apart molecular probes (EWSR1 (22q12) Break - XL, Leica Biosystem, Nussloch, Germany) showed distinct broken red and green fluorochromes, diagnostic of Ewing sarcoma. The neoplasm was characterized as adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma, and the mechanism of death was identified as airway obstruction. The rarity of the case resides in the circumstances of death, which pointed to the possibility of sudden unexpected death due to heart disease, but an oncological cause and the underlying mechanism were finally diagnosed. The best method to perform autopsies is still complete, extensive, and systematic macroscopic sampling of organs and districts followed by histopathological analysis, in addition to immunohistochemical and molecular investigations in those cases in which they are necessary. In fact, when neoplasms are detected, the application of advanced techniques such as immunohistochemistry and molecular diagnostics is fundamental to accurately certify death.
Keywords: Adamantinoma-like Ewing sarcoma; Airway occlusion; Forensic pathology; Sudden unexpected death.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declared no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

