Gene drive mosquitoes can aid malaria elimination by retarding Plasmodium sporogonic development
- PMID: 36129981
- PMCID: PMC9491717
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo1733
Gene drive mosquitoes can aid malaria elimination by retarding Plasmodium sporogonic development
Abstract
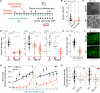
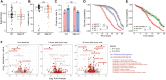
Gene drives hold promise for the genetic control of malaria vectors. The development of vector population modification strategies hinges on the availability of effector mechanisms impeding parasite development in transgenic mosquitoes. We augmented a midgut gene of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae to secrete two exogenous antimicrobial peptides, magainin 2 and melittin. This small genetic modification, capable of efficient nonautonomous gene drive, hampers oocyst development in both Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium berghei. It delays the release of infectious sporozoites, while it simultaneously reduces the life span of homozygous female transgenic mosquitoes. Modeling the spread of this modification using a large-scale agent-based model of malaria epidemiology reveals that it can break the cycle of disease transmission across a range of transmission intensities.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization, World Malaria Report 2020: 20 Years of Global Progress and Challenges (World Health Organization, 2020).
-
- Hammond A., Galizi R., Kyrou K., Simoni A., Siniscalchi C., Katsanos D., Gribble M., Baker D., Marois E., Russell S., Burt A., Windbichler N., Crisanti A., Nolan T., A CRISPR-Cas9 gene drive system targeting female reproduction in the malaria mosquito vector Anopheles gambiae. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 78–83 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

