Defensins: defenders of human reproductive health
- PMID: 36130055
- PMCID: PMC9825273
- DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmac032
Defensins: defenders of human reproductive health
Abstract
Background: Reproductive tract infection is an important factor leading to male and female infertility. Among female infertility factors, microbial and viral infections are the main factors affecting female reproductive health and causing tubal infertility, ectopic tubal pregnancy and premature delivery. Among male infertility factors, 13-15% of male infertility is related to infection. Defensins are cationic antibacterial and antiviral peptides, classified into α-defensins, β-defensins and θ-defensins. Humans only have α-defensins and β-defensins. Apart from their direct antimicrobial functions, defensins have an immunomodulatory function and are involved in many physiological processes. Studies have shown that defensins are widely distributed in the female reproductive tract (FRT) and male reproductive tract (MRT), playing a dual role of host defence and fertility protection. However, to our knowledge, the distribution, regulation and function of defensins in the reproductive tract and their relation to reproduction have not been reviewed.
Objective and rationale: This review summarizes the expression, distribution and regulation of defensins in the reproductive tracts to reveal the updated research on the dual role of defensins in host defence and the protection of fertility.
Search methods: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed using the related keywords through April 2022. Related data from original researches and reviews were integrated to comprehensively review the current findings and understanding of defensins in the human reproductive system. Meanwhile, female and male transcriptome data in the GEO database were screened to analyze defensins in the human reproductive tracts.
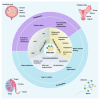
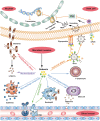
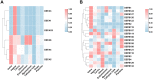
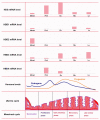
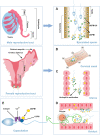
Outcomes: Two transcriptome databases from the GEO database (GSE7307 and GSE150852) combined with existing researches reveal the expression levels and role of the defensins in the reproductive tracts. In the FRT, a high expression level of α-defensin is found, and the expression levels of defensins in the vulva and vagina are higher than those in other organs. The expression of defensins in the endometrium varies with menstrual cycle stages and with microbial invasion. Defensins also participate in the local immune response to regulate the risk of spontaneous preterm birth. In the MRT, a high expression level of β-defensins is also found. It is mainly highly expressed in the epididymal caput and corpus, indicating that defensins play an important role in sperm maturation. The expression of defensins in the MRT varies with androgen levels, age and the status of microbial invasion. They protect the male reproductive system from bacterial infections by neutralizing lipopolysaccharide and downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, animal and clinical studies have shown that defensins play an important role in sperm maturation, motility and fertilization.
Wider implications: As a broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide without drug resistance, defensin has great potential for developing new natural antimicrobial treatments for reproductive tract infections. However, increasing evidence has shown that defensins can not only inhibit microbial invasion but can also promote the invasion and adhesion of some microorganisms in certain biological environments, such as human immunodeficiency virus. Therefore, the safety of defensins as reproductive tract anti-infective drugs needs more in-depth research. In addition, the modulatory role of defensins in fertility requires more in-depth research since the current conclusions are based on small-size samples. At present, scientists have made many attempts at the clinical transformation of defensins. However, defensins have problems such as poor stability, low bioavailability and difficulties in their synthesis. Therefore, the production of safe, effective and low-cost drugs remains a challenge.
Keywords: antibacterial; antivirus; defensin; fertility; immunomodulation; infertility; maternal–fetal interface; premature delivery; reproductive tract; sperm.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Figures

References
-
- Abe S, Miura K, Kinoshita A, Mishima H, Miura S, Yamasaki K, Hasegawa Y, Higashijima A, Jo O, Sasaki K. et al. Copy number variation of the antimicrobial-gene, defensin beta 4, is associated with susceptibility to cervical cancer. J Hum Genet 2013;58:250–253. - PubMed
-
- Agerberth B, Charo J, Werr J, Olsson B, Idali F, Lindbom L, Kiessling R, Jörnvall H, Wigzell H, Gudmundsson GH.. The human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides LL-37 and alpha-defensins are expressed by specific lymphocyte and monocyte populations. Blood 2000;96:3086–3093. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Jiménez W, Zapata W, Rugeles MT.. Differential expression of human beta defensins in placenta and detection of allelic variants in the DEFB1 gene from HIV-1 positive mothers. Biomedica 2011;31:44–54. - PubMed
-
- Akinbi HT, Narendran V, Pass AK, Markart P, Hoath SB.. Host defense proteins in vernix caseosa and amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;191:2090–2096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

