A de novo matrix for macroscopic living materials from bacteria
- PMID: 36130968
- PMCID: PMC9492681
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33191-2
A de novo matrix for macroscopic living materials from bacteria
Abstract
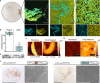
Engineered living materials (ELMs) embed living cells in a biopolymer matrix to create materials with tailored functions. While bottom-up assembly of macroscopic ELMs with a de novo matrix would offer the greatest control over material properties, we lack the ability to genetically encode a protein matrix that leads to collective self-organization. Here we report growth of ELMs from Caulobacter crescentus cells that display and secrete a self-interacting protein. This protein formed a de novo matrix and assembled cells into centimeter-scale ELMs. Discovery of design and assembly principles allowed us to tune the composition, mechanical properties, and catalytic function of these ELMs. This work provides genetic tools, design and assembly rules, and a platform for growing ELMs with control over both matrix and cellular structure and function.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetically Modifying the Protein Matrix of Macroscopic Living Materials to Control Their Structure and Rheological Properties.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Dec 20;13(12):3936-3947. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00336. Epub 2024 Nov 27. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 39601053
-
Engineering the S-Layer of Caulobacter crescentus as a Foundation for Stable, High-Density, 2D Living Materials.ACS Synth Biol. 2019 Jan 18;8(1):181-190. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00448. Epub 2019 Jan 7. ACS Synth Biol. 2019. PMID: 30577690 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering High-Yield Biopolymer Secretion Creates an Extracellular Protein Matrix for Living Materials.mSystems. 2021 Mar 23;6(2):e00903-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00903-20. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 33758029 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Engineered Living Materials: Growing Functional Materials with Genetically Programmable Properties.ACS Synth Biol. 2019 Jan 18;8(1):1-15. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00423. Epub 2019 Jan 9. ACS Synth Biol. 2019. PMID: 30576101 Review.
-
Engineered living materials (ELMs) design: From function allocation to dynamic behavior modulation.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Oct;70:102188. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102188. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35970133 Review.
Cited by
-
Secretion-Catalyzed Assembly of Protein Biomaterials on a Bacterial Membrane Surface.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023 Sep 11;62(37):e202305178. doi: 10.1002/anie.202305178. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023. PMID: 37469298 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging enzyme surface display systems for waste resource recovery.Environ Microbiol. 2023 Feb;25(2):241-249. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.16284. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36369958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of living materials via extracellular electron transfer.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Oct;20(10):1329-1340. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01628-y. Epub 2024 May 23. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38783133
-
Bacterial Species in Engineered Living Materials: Strategies and Future Directions.Microb Biotechnol. 2025 May;18(5):e70164. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70164. Microb Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40407296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synchronized Swarmers and Sticky Stalks: Caulobacter crescentus as a Model for Bacterial Cell Biology.J Bacteriol. 2023 Feb 22;205(2):e0038422. doi: 10.1128/jb.00384-22. Epub 2023 Jan 30. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 36715542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tang, T.-C. et al. Materials design by synthetic biology. Nat. Rev. Mat.10.1038/s41578-020-00265-w (2020).

