Failure of human rhombic lip differentiation underlies medulloblastoma formation
- PMID: 36131014
- PMCID: PMC10026724
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05215-w
Failure of human rhombic lip differentiation underlies medulloblastoma formation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Failure of human rhombic lip differentiation underlies medulloblastoma formation.Nature. 2022 Dec;612(7940):E12. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05578-0. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36446943 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Medulloblastoma (MB) comprises a group of heterogeneous paediatric embryonal neoplasms of the hindbrain with strong links to early development of the hindbrain1-4. Mutations that activate Sonic hedgehog signalling lead to Sonic hedgehog MB in the upper rhombic lip (RL) granule cell lineage5-8. By contrast, mutations that activate WNT signalling lead to WNT MB in the lower RL9,10. However, little is known about the more commonly occurring group 4 (G4) MB, which is thought to arise in the unipolar brush cell lineage3,4. Here we demonstrate that somatic mutations that cause G4 MB converge on the core binding factor alpha (CBFA) complex and mutually exclusive alterations that affect CBFA2T2, CBFA2T3, PRDM6, UTX and OTX2. CBFA2T2 is expressed early in the progenitor cells of the cerebellar RL subventricular zone in Homo sapiens, and G4 MB transcriptionally resembles these progenitors but are stalled in developmental time. Knockdown of OTX2 in model systems relieves this differentiation blockade, which allows MB cells to spontaneously proceed along normal developmental differentiation trajectories. The specific nature of the split human RL, which is destined to generate most of the neurons in the human brain, and its high level of susceptible EOMES+KI67+ unipolar brush cell progenitor cells probably predisposes our species to the development of G4 MB.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
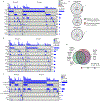




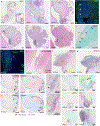


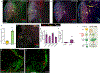
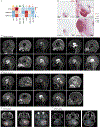


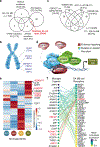
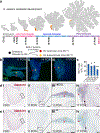
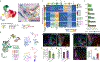
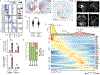

Comment in
-
The origins of medulloblastoma tumours in humans.Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7929):901-903. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02951-x. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36131054 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wechsler-Reya RJ & Scott MP Control of Neuronal Precursor Proliferation in the Cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog. Neuron 22, 103–114 (1999). - PubMed
ONLINE-ONLY REFERENCES
-
- Milde T. et al. HD-MB03 is a novel Group 3 medulloblastoma model demonstrating sensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitor treatment. J. Neurooncol 110, 335–348 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS113516/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS122902/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080390/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA235162/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA255369/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS117848/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS095733/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS095733/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/R006237/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 CA196539/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS106155/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA159859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA096832/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

