Efficacy of arterial spin labeling for detection of the ruptured micro-arteriovenous malformation: illustrative cases
- PMID: 36131567
- PMCID: PMC9379700
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE21597
Efficacy of arterial spin labeling for detection of the ruptured micro-arteriovenous malformation: illustrative cases
Abstract
Background: Diagnosis of a microarteriovenous malformation (micro-AVM) is difficult, especially in the acute stage of rupture because of the small size of the nidus and the existence of hematoma. We report two cases of ruptured micro-AVMs detected by arterial spin labeling (ASL).
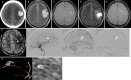
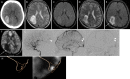
Observations: In one case, a 45-year-old male was transported with a complaint of right hemiparesis. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a right parietal lobar hemorrhage. Standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed no abnormal findings as the cause of the hemorrhage. ASL 23 days after the onset demonstrated high signals on the medial wall of the hematoma. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) showed a micro-AVM in accordance with the site of high signals on ASL. In another case, a 38-year-old female was transported with a complaint of left hemianopsia. CT on admission revealed a right parietal lobar hemorrhage. Standard MRI showed no abnormal findings as the cause of the hemorrhage. ASL 15 days after the onset demonstrated high signals on the internal wall of the hematoma. DSA showed micro-AVM in accordance with the site of high signaling on ASL. Both cases were successfully treated with open surgery.
Lessons: ASL can manifest micro-AVMs as high signals within the hematoma. ASL is a useful less-invasive screening tool for the detection of ruptured micro-AVMs.
Keywords: arterial spin labeling; intracerebral hematoma; micro-arteriovenous malformation; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of repeat arterial spin labeling for angiogram-negative ruptured micro-arteriovenous malformation: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2023 Mar 31;14:119. doi: 10.25259/SNI_200_2023. eCollection 2023. Surg Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37151432 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging: toward noninvasive diagnosis and follow-up of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015 Apr;15(4):451-8. doi: 10.3171/2014.9.PEDS14194. Epub 2015 Jan 30. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25634818
-
Evaluation of obliteration of arteriovenous malformations after stereotactic radiosurgery with arterial spin labeling MR imaging.Br J Neurosurg. 2017 Dec;31(6):641-647. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2017.1365818. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Br J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28830253
-
Gross Total Resection of a Ruptured Micro-arteriovenous Malformation within the Cerebellar Peduncle: A Case Report and Qualitative Review of the Literature.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2023 Nov;84(6):600-605. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1744299. Epub 2022 May 29. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 35644136 Review.
-
Ruptured Distal Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA) Aneurysms Associated with Cerebellar Arterial Venous Malformations (AVMs): A Case Series and Review of the Literature Demonstrating the Need for Angiographic Evaluation and Feasibility of Endovascular Treatment.World Neurosurg. 2017 Jan;97:751.e7-751.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.10.081. Epub 2016 Oct 25. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27793767 Review.
Cited by
-
Arterial Spin Labeling: Key Concepts and Progress Towards Use as a Clinical Tool.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2024 Jul 1;23(3):352-366. doi: 10.2463/mrms.rev.2024-0013. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38880616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of repeat arterial spin labeling for angiogram-negative ruptured micro-arteriovenous malformation: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2023 Mar 31;14:119. doi: 10.25259/SNI_200_2023. eCollection 2023. Surg Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37151432 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Future Applications of Arterial Spin Labeling MRI in Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 28;12(4):753. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040753. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Detre JA, Alsop DC, Vives LR, Maccotta L, Teener JW, Raps EC. Noninvasive MRI evaluation of cerebral blood flow in cerebrovascular disease. Neurology. 1998;50(3):633–641. - PubMed
-
- Shimogawa T, Morioka T, Sayama T, et al. The initial use of arterial spin labeling perfusion and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images in the diagnosis of nonconvulsive partial status epileptics. Epilepsy Res. 2017;129:162–173. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

