Defining tourniquetless total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review
- PMID: 36131796
- PMCID: PMC9483623
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.09.003
Defining tourniquetless total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Performing total knee arthroplasty (TKA) without the use of tourniquet is gaining popularity. However, performing a "tourniquetless TKA" has a variety of meanings regarding the timing and application of a tourniquet and associated techniques. The purpose of this systematic review was to evaluate the literature and more accurately define "tourniquetless TKA."
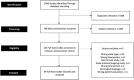
Methods: A systematic review following PRISMA guidelines was performed of the PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases for articles published from 2016 to 2021. Inclusion criteria included papers that used "tourniquetless" or a similar term to describe their TKA procedure, original clinical studies, English language, and full-text studies.
Results: A total of 1,096 studies were identified, of which 84 full text studies with 9,349 total patients were included. Overall, 17 (20.2%) of the studies performing tourniquetless TKA never applied a tourniquet, 17 (20.2%) applied a tourniquet but kept it deflated throughout the entire procedure, 2 (2.4%) applied a tourniquet and inflated during cementation only, and 48 (57.1%) did not specify. Ultimately, of the studies that did specify tourniquet use, only 17 studies (47.2%) truly never applied a tourniquet throughout the procedure. A review of 7 recommended techniques to control blood loss in tourniquetless TKA found that no one technique was performed in more than 10.6% of patients.
Conclusion: Variation in the definition of tourniquetless TKA and the utilization of augmented techniques to control blood loss remains. We propose the terms "tourniquetless" for no tourniquet application, "tourniquet-available" for tourniquet applied but kept deflated throughout surgery, and "tourniquet-assisted" for tourniquet inflation during cementation only. These terms can help better differentiate the literature, guide surgeons as they transition to tourniquetless TKA, and assist in the development of more definitive protocols for tourniquetless TKA.
Keywords: Blood loss; Hemostasis; Systematic review; TKA; TKA, Total Knee Arthroplasty; Total knee arthroplasty; Tourniquet; Tourniquetless.
© 2022 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Senior author VH declares paid consultation for Stryker, Pfizer, and Consensus, as well as roles as a voting member of the AAHKS International Committee and Editor of JBJS CME. No other authors have any financial disclosures nor declare any conflicts of interest.
References
-
- No authors listed . 2012. Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register Annual Report 2012. Lund, Sweden.
-
- Abdel M.P., Berry D.J. Current practice trends in primary Hip and knee arthroplasties among members of the American association of Hip and knee surgeons: a long-term update. J Arthroplasty. 2019 Jul;34(7):S24–S27. - PubMed
-
- Pfitzner T., von Roth P., Voerkelius N., Mayr H., Perka C., Hube R. Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 Jan 25;24(1):96–101. - PubMed
-
- Alcelik I., Pollock R.D., Sukeik M., Bettany-Saltikov J., Armstrong P.M., Fismer P. A comparison of outcomes with and without a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012 Mar;27(3):331–340. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources