Inorganic-organic core/shell nanoparticles: progress and applications
- PMID: 36132014
- PMCID: PMC9419210
- DOI: 10.1039/d0na00411a
Inorganic-organic core/shell nanoparticles: progress and applications
Abstract
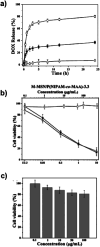
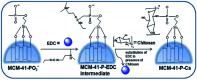
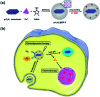
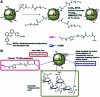
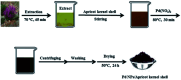
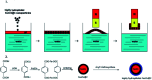
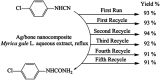
In recent decades a great deal of research has been dedicated to the development of core-shell nanoparticles (NPs). We decided to focus our attention on NPs with inorganic cores and organic shells and divide them by area of application such as electrical applications, drug delivery, biomedical applications, imaging, chemistry and catalysis. Organic shells, consisting in most cases of polymers (natural or synthetic), proteins or complex sugars, can improve the performance of inorganic NPs by enhancing their biocompatibility, acting as anchor sites for molecular linkages or protecting them from oxidation. Moreover, suitable design of the shell thickness can improve the chemical and thermal stability of NPs together with the possibility of tuning and controlling the release of molecules from the core. In the future new discoveries will guarantee improvement in the properties of NPs, synthesis, and applications of this class of nanomaterials that are constantly evolving.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Shell-by-Shell Functionalization of Inorganic Nanoparticles.Chemistry. 2020 Jul 14;26(39):8483-8498. doi: 10.1002/chem.202000195. Epub 2020 May 14. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 32167598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Core-Shell Magnetic Particles: Tailored Synthesis and Applications.Chem Rev. 2025 Jan 22;125(2):972-1048. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00710. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 39729245 Review.
-
Functional DNA Molecules Enable Selective and Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2415-2426. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00167. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31411853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Composite Layer-by-Layer (LBL) assembly with inorganic nanoparticles and nanowires.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Dec;41(12):1831-41. doi: 10.1021/ar8001377. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 19053241
-
Amphiphilic core-shell nanoparticles: Synthesis, biophysical properties, and applications.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 Dec 1;172:68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 30138789 Review.
Cited by
-
Hybrid Inorganic-Organic Core-Shell Nanodrug Systems in Targeted Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 23;13(11):1773. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111773. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inorganic Nanoparticles in Bone Healing Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 31;14(4):770. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040770. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology in healthcare, and its safety and environmental risks.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Nov 15;22(1):715. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02901-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39548502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Biomaterials for Safeguarding Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: An Artful Expedition in Mitigating Adverse Effects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;17(1):139. doi: 10.3390/ph17010139. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Switchable aqueous catalytic systems for organic transformations.Commun Chem. 2022 Sep 26;5(1):115. doi: 10.1038/s42004-022-00734-z. Commun Chem. 2022. PMID: 36697818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu H. L. Hou P. Zhang W. X. Wu J. H. Colloid. Surface. Physicochem. Eng. Aspect. 2010;356:21–27. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.12.023. - DOI
-
- Hoener C. F. Allan K. A. Bard A. J. Campion A. Fox M. A. Mallouk T. E. Webber S. E. White J. M. J. Phys. Chem. 1992;96:3812–3817. doi: 10.1021/j100188a045. - DOI
-
- Honma I. Sano T. Komiyama H. J. Phys. Chem. 1993;97:6692–6695. doi: 10.1021/j100127a020. - DOI
-
- Zhou H. S. Sasahara H. Honma I. Komiyama H. Haus J. W. Chem. Mater. 1994;6:1534–1541. doi: 10.1021/cm00045a010. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

