A review on health benefits of phenolics derived from dietary spices
- PMID: 36132490
- PMCID: PMC9483645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.09.009
A review on health benefits of phenolics derived from dietary spices
Abstract
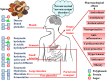
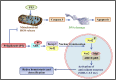
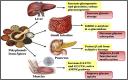
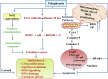
Spices are an affluentpool of polyphenolcompounds that possessgigantic medicinal peculiarities such as remedying microbial infections, oxidative stress, inflammation, diabetes, cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, cardiac disorders, etc. On that account, thepresent review illustrates the therapeutic potential, mechanism of action, and different procedures for conscious extraction of polyphenols. The various ethnopharmacological properties; reasons for their diverse pharmacological actions and the mechanism of action of spices-derived phenolics have also been discussed. The findings of this review may be utilized by the food and pharmaceutical industries for developing suitable alternatives to synthetic antioxidants and can be developed into effective food supplements. Further in-depth scientific studies are needed to find out their actual and exact relevance as natural health boosters. Moreover, clinical and toxicological studies are also required for harnessing the full therapeutic potential of polyphenols derived from dietary spices.
Keywords: Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Pharmacology; Polyphenols; Secondary metabolites; Spices.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Assefa A.D., Keum Y.S., Saini R.K. A comprehensive study of polyphenols contents and antioxidant potential of 39 widely used spices and food condiments. J. Food Meas. Char. 2018;12:1548–1555. doi: 10.1007/s11694-018-9770-z. - DOI
-
- Basli A., Belkacem N., Amrani I. Marcos Soto-Hernández, Rosario García-Mateos and Mariana Palma-Tenango. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2017. Health benefits of phenolic compounds against cancers; pp. 193–210. (In Phenolic Compounds–Biological Activity). - DOI
-
- BettaiebRebey I., Bourgou S., Aidi Wannes W., HamrouniSelami I., SaidaniTounsi M., Marzouk B., Ksouri R. Comparative assessment of phytochemical profiles and antioxidant properties of Tunisian and Egyptian anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) seeds. Plant Biosystems-an International Journal Dealing with All Aspects of Plant Biology. 2018;152:971–978. doi: 10.1080/11263504.2017.1403394. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

