Optimal centrifugal isolating of liposome-protein complexes from human plasma
- PMID: 36133013
- PMCID: PMC9418580
- DOI: 10.1039/d1na00211b
Optimal centrifugal isolating of liposome-protein complexes from human plasma
Abstract
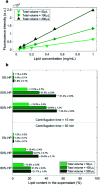
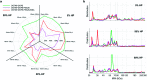
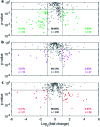
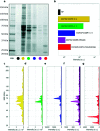
In the past few years, characterization of the protein corona (PC) that forms around liposomal systems has gained increasing interest for the development of novel therapeutic and diagnostic technologies. At the crossroads of fast-moving research fields, the interdisciplinarity of protein corona investigations poses challenges for experimental design and reporting. Isolation of liposome-protein complexes from biological fluids has been identified as a fundamental step of the entire workflow of PC characterization but exact specifications for conditions to optimize pelleting remain elusive. In the present work, key factors affecting precipitation of liposome-protein complexes by centrifugation, including time of centrifugation, total sample volume, lipid : protein ratio and contamination from biological NPs were comprehensively evaluated. Here we show that the total amount of isolated liposome-protein complexes and the extent of contamination from biological NPs may vary with influence factors. Our results provide protein corona researchers with precise indications to separate liposome-protein complexes from protein-rich fluids and include proper controls, thus they are anticipated to catalyze improved consistency of data mining and computational modelling of protein corona composition.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Comment in
-
Comment on "Optimal centrifugal isolating of liposome-protein complexes from human plasma" by L. Digiacomo, F. Giulimondi, A. L. Capriotti, S. Piovesana, C. M. Montone, R. Z. Chiozzi, A. Laganá, M. Mahmoudi, D. Pozzi and G. Caracciolo, Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3, 3824.Nanoscale Adv. 2022 Nov 30;5(1):290-299. doi: 10.1039/d2na00343k. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. Nanoscale Adv. 2022. PMID: 36605796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J. Zhang R. Xu Z. P. Small. 2019:1900262. doi: 10.1002/smll.201900262. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

