Photothermal release of an encapsulated therapeutic agent from polymer-wrapped gold nanoparticles
- PMID: 36134313
- PMCID: PMC9419036
- DOI: 10.1039/d1na00289a
Photothermal release of an encapsulated therapeutic agent from polymer-wrapped gold nanoparticles
Abstract
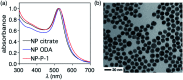
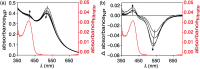
Visible light is used to generate heat from gold nanoparticles wrapped in an amphiphilic polymer shell and trigger a reverse Diels-Alder reaction of a 'caged' tyrphostin therapeutic agent. The hydrophilic nature of the released agent results in it travelling from the polymer to the bulk medium, while the byproduct of the reaction is trapped in the hydrophobic layer of the nano-assembly.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NIR and glutathione trigger the surface release of methotrexate linked by Diels-Alder adducts to anisotropic gold nanoparticles.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Dec;131:112512. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112512. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 34857291
-
Two colors of light are needed to break bonds and release small molecules from the surface of SiO2-Au core-shell nanoparticles.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Mar 4;137(8):2824-7. doi: 10.1021/ja513210s. Epub 2015 Feb 23. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25686633
-
Controlled-release system mediated by a retro Diels-Alder reaction induced by the photothermal effect of gold nanorods.Langmuir. 2011 Dec 6;27(23):14621-6. doi: 10.1021/la2036746. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Langmuir. 2011. PMID: 21988322
-
[Drug release system controlled by near infrared light].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(3):369-72. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.12-00239-3. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 23449416 Review. Japanese.
-
[Drug Release System Controlled by Photothermal Effect of Gold Nanoparticles].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2021;141(3):327-332. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00179-4. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2021. PMID: 33642499 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Mathiowitz E. Cohen M. J. Membr. Sci. 1989;40:67. doi: 10.1016/S0376-7388(00)80913-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

