Recent advances in mechanical force-responsive drug delivery systems
- PMID: 36134346
- PMCID: PMC9400598
- DOI: 10.1039/d2na00420h
Recent advances in mechanical force-responsive drug delivery systems
Abstract
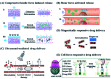
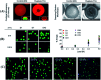
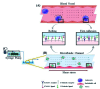
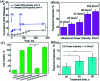
Mechanical force responsive drug delivery systems (in terms of mechanical force induced chemical bond breakage or physical structure destabilization) have been recently explored to exhibit a controllable pharmaceutical release behaviour at a molecular level. In comparison with chemical or biological stimulus triggers, mechanical force is not only an external but also an internal stimulus which is closely related to the physiological status of patients. However, although this mechanical force stimulus might be one of the most promising and feasible sources to achieve on-demand pharmaceutical release, current research in this field is still limited. Hence, this tutorial review aims to comprehensively evaluate the recent advances in mechanical force-responsive drug delivery systems based on different types of mechanical force, in terms of direct stimulation by compressive, tensile, and shear force, or indirect/remote stimulation by ultrasound and a magnetic field. Furthermore, the exciting developments and current challenges in this field will also be discussed to provide a blueprint for potential clinical translational research of mechanical force-responsive drug delivery systems.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Mechanical Force-Triggered Drug Delivery.Chem Rev. 2016 Oct 12;116(19):12536-12563. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00369. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 27680291 Review.
-
Polymer mechanochemistry in drug delivery: From controlled release to precise activation.J Control Release. 2023 Oct 27:S0168-3659(23)00703-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.10.042. Online ahead of print. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 39491171 Review.
-
Smart micro/nanoparticles in stimulus-responsive drug/gene delivery systems.Chem Soc Rev. 2016 Mar 7;45(5):1457-501. doi: 10.1039/c5cs00798d. Chem Soc Rev. 2016. PMID: 26776487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks as Anticancer Drug Delivery Systems: A Review.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(18):2487-2504. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210119093844. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33463479 Review.
-
Intellective and stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems in eyes.Int J Pharm. 2021 Jun 1;602:120591. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120591. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33845152 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of mechanical forces on cellular response to radiation.Radiother Oncol. 2022 Nov;176:187-198. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.10.006. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Radiother Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36228760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote Positioning of Spherical Alginate Ferrogels in a Fluid Flow by a Magnetic Field: Experimental and Computer Simulation.Gels. 2023 Sep 1;9(9):711. doi: 10.3390/gels9090711. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37754392 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Reservoirs Enabling Stress-Induced Sequential Release Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 26;14(12):2611. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122611. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559107 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer theragnostics: closing the loop for advanced personalized cancer treatment through the platform integration of therapeutics and diagnostics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 17;12:1499474. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1499474. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39898278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent applications of stimulus-responsive smart hydrogels for osteoarthritis therapy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 17;13:1539566. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1539566. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40035023 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rozenbaum R. T. Andrén O. C. J. van der Mei H. C. Woudstra W. Busscher H. J. Malkoch M. Sharma P. K. Penetration and Accumulation of Dendrons with Different Peripheral Composition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Nano Lett. 2019;19(7):4327–4333. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00838. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque L. J. C. Sincari V. Jäger A. Kucka J. Humajova J. Pankrac J. Paral P. Heizer T. Janouškova O. Davidovich I. Talmon Y. Pouckova P. Štěpánek P. Sefc L. Hruby M. Giacomelli F. C. Jäger E. pH-responsive polymersome-mediated delivery of doxorubicin into tumor sites enhances the therapeutic efficacy and reduces cardiotoxic effects. J. Controlled Release. 2021;332:529–538. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

