Sculpting an Embryo: The Interplay between Mechanical Force and Cell Division
- PMID: 36135370
- PMCID: PMC9502278
- DOI: 10.3390/jdb10030037
Sculpting an Embryo: The Interplay between Mechanical Force and Cell Division
Abstract
The journey from a single fertilised cell to a multicellular organism is, at the most fundamental level, orchestrated by mitotic cell divisions. Both the rate and the orientation of cell divisions are important in ensuring the proper development of an embryo. Simultaneous with cell proliferation, embryonic cells constantly experience a wide range of mechanical forces from their surrounding tissue environment. Cells must be able to read and respond correctly to these forces since they are known to affect a multitude of biological functions, including cell divisions. The interplay between the mechanical environment and cell divisions is particularly crucial during embryogenesis when tissues undergo dynamic changes in their shape, architecture, and overall organisation to generate functional tissues and organs. Here we review our current understanding of the cellular mechanisms by which mechanical force regulates cell division and place this knowledge within the context of embryogenesis and tissue morphogenesis.
Keywords: biomechanics; cell division; cell division orientation; cell division rate; cell shape; embryogenesis; mechanical force; mitosis; mitotic spindle; morphogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
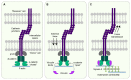


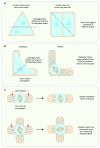


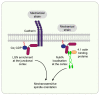
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

