Paecilomyces/ Purpureocillium Infection in Children, Case Report, and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 36135655
- PMCID: PMC9501290
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8090930
Paecilomyces/ Purpureocillium Infection in Children, Case Report, and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Paecilomyces/Purpureocillium has recently been recognized as an emerging human pathogen, causing serious infection in immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. Several predisposing factors have been reported, including foreign body implants, previous surgery, or trauma. Treatment with antifungal drugs often fails as species-specific differences in antifungal susceptibilities are one of the management challenges. Surgical debridement with or without antifungal therapy was sufficient to cure the infection in a few reported cases. Nonetheless, the surgical approach has been found to decrease the chance of dissemination and recurrence. Here, we report the first pediatric patient with chronic osteomyelitis of the femur secondary to Paecilomyces species, with no predisposing risk factors. Our case was successfully treated with a combination of antifungal therapy and surgical debridement. Additionally, we describe the first extensive literature review of previously reported Paecilomyces/Purpureocillium species infections in pediatric age groups.
Keywords: Paecilomyces; Purpureocillium; fungal; immunocompetent; osteomyelitis; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
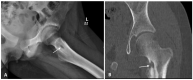
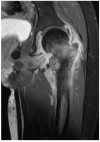
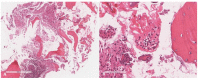
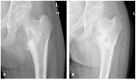
Similar articles
-
Paecilomyces/Purpureocillium keratitis: A consecutive study with a case series and literature review.Med Mycol. 2020 Apr 1;58(3):293-299. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myz059. Med Mycol. 2020. PMID: 31204788 Review.
-
Cutaneous infection caused by Purpureocillium lilacinum: Case reports and literature review of infections by Purpureocillium and Paecilomyces in Taiwan.J Dermatol. 2023 Aug;50(8):1088-1092. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16806. Epub 2023 Apr 20. J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37082787 Review.
-
Keratomycosis due to Purpureocillium lilacinum: A case report from Sub-Himalayan region of Uttarakhand.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018 Oct-Dec;61(4):607-609. doi: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_404_17. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30303164
-
Cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis caused by Paecilomyces lilacinus in an immunocompetent host successfully treated with itraconazole: case report and review.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999 Nov;18(11):814-8. doi: 10.1007/s100960050407. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999. PMID: 10614958 Review.
-
Purpureocillium, a new genus for the medically important Paecilomyces lilacinus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011 Aug;321(2):141-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02322.x. Epub 2011 Jun 23. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21631575
References
-
- Sprute R., Salmanton-García J., Sal E., Malaj X., Falces-Romero I., Hatvani L., Heinemann M., Klimko N., López-Soria L., Meletiadis J., et al. Characterization and outcome of invasive infections due to Paecilomyces variotii: Analysis of patients from the FungiScope® registry and literature reports. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021;76:765–774. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa481. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

