Zearalenone and Its Masked Forms in Cereals and Cereal-Derived Products: A Review of the Characteristics, Incidence, and Fate in Food Processing
- PMID: 36135701
- PMCID: PMC9501528
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8090976
Zearalenone and Its Masked Forms in Cereals and Cereal-Derived Products: A Review of the Characteristics, Incidence, and Fate in Food Processing
Abstract
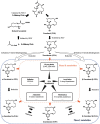
Zearalenone (ZEA) is known as a Fusarium-produced mycotoxin, representing a risk to cereal food safety with repercussions for economies and worldwide trade. Recent studies have reported the co-occurrence of ZEA and masked ZEA in a variety of cereals and cereal-based products, which may exert adverse effects on public health due to additive/synergistic interactions. However, the co-contamination of ZEA and masked ZEA has received little attention. In order to minimize the threats of co-contamination by ZEA and masked ZEA, it is necessary to recognize the occurrence and formation of ZEA and masked ZEA. This review focuses on the characteristics, incidence, and detection of ZEA and its masked forms. Additionally, the fate of ZEA and masked ZEA during the processing of bread, cake, biscuits, pasta, and beer, as well as the ZEA limit, are discussed. The incidence of masked ZEA is lower than that of ZEA, and the mean level of masked ZEA varies greatly between cereal samples. Published data showed a considerable degree of heterogeneity in the destiny of ZEA during cereal-based food processing, mostly as a result of the varying contamination levels and complicated food processing methods. Knowledge of the fate of ZEA and masked ZEA throughout cereal-based food processing may reduce the likelihood of severe detrimental market and trade ramifications. The revision of legislative limits of masked ZEA may become a challenge in the future.
Keywords: cereal and cereal-based food; characteristic; food processing; incidence; zearalenone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fast R.B., Caldwell E.F. Breakfast Cereals, and How They Are Made. American Association of Cereal Chemists; Eagan, MN, USA: 2000.
-
- Nematollahi A., Kamankesh M., Hosseini H., Ghasemi J., Hosseini-Esfahani F., Mohammadi A. Investigation and determination of acrylamide in the main group of cereal products using advanced microextraction method coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Cereal Sci. 2019;87:157–164. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2019.03.019. - DOI
-
- Faltermaier A., Waters D., Becker T., Arendt E., Gastl M. Common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and its use as a brewing cereal—A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014;120:1–15. doi: 10.1002/jib.107. - DOI
-
- Khaneghah A.M., Martins L.M., von Hertwig A.M., Bertoldo R., Sant’Ana A.S. Deoxynivalenol and its masked forms: Characteristics, incidence, control and fate during wheat and wheat based products processing—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;71:13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.10.012. - DOI
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Global Cereal Trade and Utilization in 2021/22 Revised Down. 2022. [(accessed on 9 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/worldfoodsituation/csdb/en/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources