Performance and Mechanism of As(III/V) Removal from Aqueous Solution by Fe3O4-Sunflower Straw Biochar
- PMID: 36136499
- PMCID: PMC9504546
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10090534
Performance and Mechanism of As(III/V) Removal from Aqueous Solution by Fe3O4-Sunflower Straw Biochar
Abstract
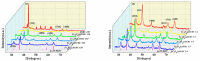
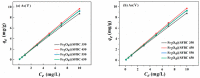
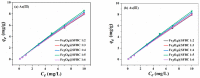
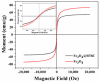
Humans and ecosystems are severely damaged by the existence of As(III/V) in the aquatic environment. Herein, an advanced Fe3O4@SFBC (Fe3O4-sunflower straw biochar) adsorbent was fabricated by co-precipitation method with sunflower straw biochar (SFBC) prepared at different calcination temperatures and different SFBC/Fe mass ratios as templates. The optimal pH for As(III/V) removal was investigated, and Fe3O4@SFBC shows removal efficiency of 86.43% and 95.94% for As(III) and As(V), respectively, at pH 6 and 4. The adsorption effect of calcining and casting the biochar-bound Fe3O4 obtained at different temperatures and different SFBC/Fe mass ratios were analyzed by batch experiments. The results show that when the SFBC biochar is calcined at 450 °C with an SFBC/Fe mass ratio of 1:5, the adsorption of As(III) and As(V) reaches the maximum, which are 121.347 and 188.753 mg/g, respectively. Fe3O4@SFBC morphology, structure, surface functional groups, magnetic moment, and internal morphology were observed by XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM, and VSM under optimal working conditions. The material shows a small particle size in the range of 12-14 nm with better magnetic properties (54.52 emu/g), which is suitable for arsenic removal. The adsorption mechanism of As(III/V) by Fe3O4@SFBC indicates the presence of chemisorption, electrostatic, and complexation. Finally, the material was used for five consecutive cycles of adsorption-desorption experiments, and no significant decrease in removal efficiency was observed. Therefore, the new adsorbent Fe3O4@SFBC can be efficiently used for arsenic removal in the aqueous system.
Keywords: As(III/V); Fe3O4; adsorption; magnetic composite; sunflower straw biochar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Bissen M., Frimmel F.H. Arsenic—A review. Part I: Occurrence, toxicity, speciation, mobility. Acta Hydroch. Hydrob. 2003;31:9–18. doi: 10.1002/aheh.200390025. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. 4th ed. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011.
Grants and funding
- 2020M673643XB/the 67th batch of general project funding from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- ZDSYS-JS-2022-13/Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Water Resources Engineering Safety and Water Disaster Prevention and Control 2022 Open Subjects
- 2022D01B20/Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 42067035, 42007161/the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NNSFC)
- XJAUGRI2022044/2022 Graduate Research Innovation Program of Xinjiang Agricultural University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

