Arabic Gum Could Alleviate the Aflatoxin B1-provoked Hepatic Injury in Rat: The Involvement of Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory, and Apoptotic Pathways
- PMID: 36136543
- PMCID: PMC9500620
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14090605
Arabic Gum Could Alleviate the Aflatoxin B1-provoked Hepatic Injury in Rat: The Involvement of Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory, and Apoptotic Pathways
Abstract
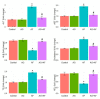
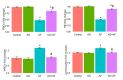
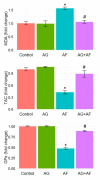
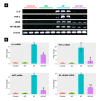
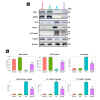
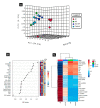
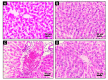
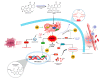
Aflatoxin B1 (AF) is an unavoidable environmental pollutant that contaminates food, feed, and grains, which seriously threatens human and animal health. Arabic gum (AG) has recently evoked much attention owing to its promising therapeutic potential. Thus, the current study was conducted to look into the possible mechanisms beyond the ameliorative activity of AG against AF-inflicted hepatic injury. Male Wistar rats were assigned into four groups: Control, AG (7.5 g/kg b.w/day, orally), AF (200 µg/kg b.w), and AG plus AF group. AF induced marked liver damage expounded by considerable changes in biochemical profile and histological architecture. The oxidative stress stimulated by AF boosted the production of plasma malondialdehyde (MDA) level along with decreases in the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) level and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity. Additionally, AF exposure was associated with down-regulation of the nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor2 (Nrf2) and superoxide dismutase1 (SOD1) protein expression in liver tissue. Apoptotic cascade has also been evoked following AF-exposure, as depicted in overexpression of cytochrome c (Cyto c), cleaved Caspase3 (Cl. Casp3), along with enhanced up-regulation of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and nuclear factor kappa-B transcription factor/p65 (NF-κB/p65) mRNA expression levels. Interestingly, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory contents of AG may reverse the induced oxidative damage, inflammation, and apoptosis in AF-exposed animals.
Keywords: Arabic gum; aflatoxin B1; apoptosis; inflammatory cytokines; liver injury; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The protective efficacy of soursop fruit extract against hepatic injury associated with acetaminophen exposure is mediated through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic activities.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 May;26(13):13539-13550. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04935-3. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30915694
-
Ameliorative effect of herbacetin against cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221132140. doi: 10.1177/09603271221132140. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36198566
-
The involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory response in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24246655
-
Antioxidant and anticancer potentials of edible flowers: where do we stand?Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(31):8589-8645. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1931022. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34096420 Review.
-
Pathological Role of Oxidative Stress in Aflatoxin-Induced Toxicity in Different Experimental Models and Protective Effect of Phytochemicals: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Jul 13;28(14):5369. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145369. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ameliorative effects of camel milk and silymarin upon aflatoxin B1 induced hepatic injury in rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 12;13(1):15092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41586-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37699912 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Studies on the Therapeutic Effect of Naja nubiae Venom Against Melamine Induced Hepatotoxicity in Albino Rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Apr 7;13(4):e70081. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70081. eCollection 2025 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40196227 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor1-alpha in the protective effect of rivaroxaban against testicular ischemia-reperfusion in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27711. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10395-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730830 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of inflammation and oxidative stress in FCA-induced arthritic rat model through gum acacia intervention: a comprehensive in‑vivo study.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01907-7. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40801980
-
Radioprotective potential of whey protein against gamma irradiation-induced lingual damage.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 13;14:1293230. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1293230. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38155907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 401/2006 Laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Comm. Regul. 2006;70:12.
-
- Abdel-Daim M.M., Abdeen A., Jalouli M., Abdelkader A., Megahed A., Alkahtane A., Almeer R., Alhoshani N.M., Al-Johani N.S., Alkahtani S., et al. Fucoidan supplementation modulates hepato-renal oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by aflatoxin B1 intoxication in rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;768:144781. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144781. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz S., Bag H. Aflatoxin B1: Mechanism, oxidative stress, and effects on animal health. Insights Vet. Sci. 2022;6:17–24. doi: 10.29328/journal.ivs.1001037. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

