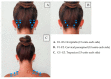
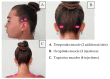
Botulinum Toxin-A Current Place in the Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Primary Headaches
- PMID: 36136557
- PMCID: PMC9501363
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14090619
Botulinum Toxin-A Current Place in the Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Primary Headaches
Abstract
Headaches are a very common condition that most people will experience many times during their lives. This article presents the primary headaches, which are a large group of diseases where the headache is not a symptom of another known disease. Tension-type headache affects approximately 80% of the general population, and the prevalence of migraine is estimated at 10-12%. Clinical data and experience to date have demonstrated that botulinum toxin may be an effective prophylactic treatment for chronic headache types. It has been used in neurology for the treatment of dystonia and blepharospasm. Now it has been approved to treat chronic migraine and has been shown to confer significant benefit in refractory cases. Based on clinical experience botulinum toxin has also been tried in other headache disorders. While it is intuitively attractive to think that due to its effect on pain by sensory modulation, there may also be efficacy in its use in chronic tension-type headache and cluster headache, so far, there is little evidence to support this. Botulinum toxin is effective in pain control through its interaction with the SNARE complex, which inhibits the release of neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide. OnabotulinumtoxinA is effective not only in headache frequency and pain intensity but in other parameters, including quality of life.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; chronic migraine; cluster headache; headaches; onabotulinumtoxinA; tension-type headache.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preventative treatment for migraine and tension-type headaches : do drugs having effects on muscle spasm and tone have a role?CNS Drugs. 2003;17(6):373-81. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200317060-00001. CNS Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12696998 Review.
-
Botulinum toxin A for prophylactic treatment of migraine and tension headaches in adults: a meta-analysis.JAMA. 2012 Apr 25;307(16):1736-45. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.505. JAMA. 2012. PMID: 22535858
-
Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin in Tension-Type Headaches: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Pain Pract. 2019 Jun;19(5):541-551. doi: 10.1111/papr.12773. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Pain Pract. 2019. PMID: 30742360
-
Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of migraine and other primary headache disorders: from bench to bedside.Headache. 2003 Jul-Aug;43 Suppl 1:S25-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1526-4610.43.7s.5.x. Headache. 2003. PMID: 12887391 Review.
-
Use of botulinum toxins for chronic headaches: a focused review.Clin J Pain. 2002 Nov-Dec;18(6 Suppl):S169-76. doi: 10.1097/00002508-200211001-00009. Clin J Pain. 2002. PMID: 12569965 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in patients with traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, or multiple sclerosis: An observational longitudinal study.Front Neurol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1133390. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1133390. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37090974 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on the Nociceptive and Lemniscal Somatosensory Systems in Chronic Migraine: An Electrophysiological Study.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 14;15(1):76. doi: 10.3390/toxins15010076. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36668895 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Targeted Subcutaneous Injection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A in Refractory Chronic Migraine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study.Toxins (Basel). 2023 May 9;15(5):324. doi: 10.3390/toxins15050324. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37235358 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic Migraine as a Primary Chronic Pain Syndrome and Recommended Prophylactic Therapeutic Options: A Literature Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;13(3):665. doi: 10.3390/life13030665. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness and predictors influencing the outcome of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in chronic migraine: understanding from diverse patient profiles in a single session.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1417303. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1417303. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38962481 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical